Nov 16, 2024
An Asteroid Hit Earth Just Hours After Being Detected
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in categories: asteroid/comet impacts, existential risks
A small asteroid burned up in Earth’s atmosphere off the coast of California just hours after being discovered and before impact monitoring systems had registered its trajectory.
Last month, an asteroid impacted Earth’s atmosphere just hours after being detected — somehow, it managed to circumvent impact monitoring systems during its approach to our planet. However, on the bright side, the object measured just 3 feet (1 meter) in diameter and posed very little threat to anything on Earth’s surface.
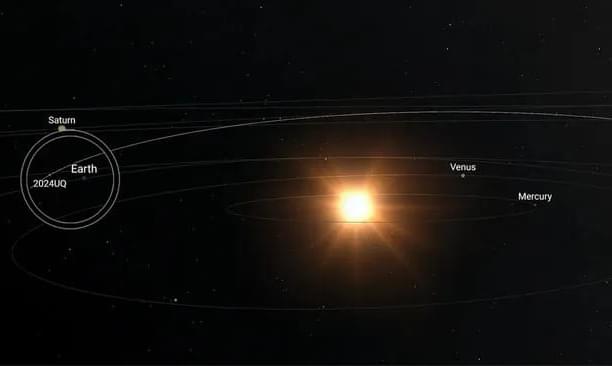
This asteroid, designated 2024 UQ, was first discovered on Oct. 22 by the Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System (ATLAS) survey in Hawaii, a network of four telescopes that scan the sky for moving objects that might be space rocks on a collision course with Earth. Two hours later, the asteroid burned up over the Pacific Ocean near California, making it an “imminent impactor.”