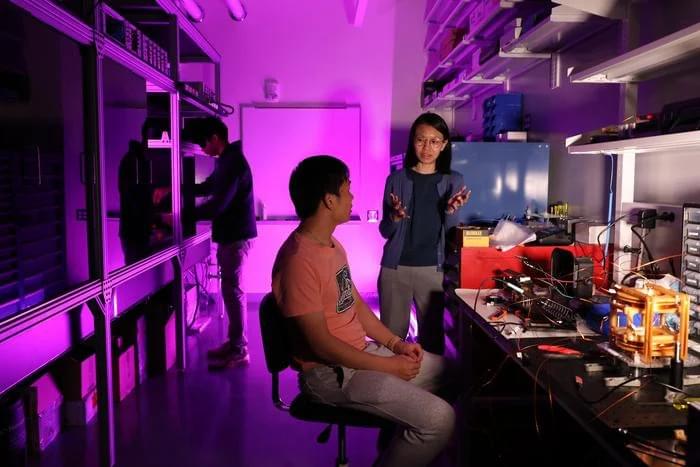
Lithium-metal batteries (LMBs) are rechargeable batteries that contain an anode (i.e., the electrode through which current flows and a loss of electrons occurs) made of lithium metal. Compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries (LIBs), which power most electronic devices on the market today, LMBs could store more energy, charge faster and operate in extreme environments.
Despite their advantages, these batteries have not yet achieved their full potential and recharging them safely in short periods of time has proved challenging. In particular, enabling the fast and efficient movement of electrons and ions across the boundary between electrodes and the electrolyte, a process known as charge transfer, has proved difficult.
If charge transfer is slow, chemical reactions become sluggish, which can also lead to undesirable side reactions and prompt the formation of Li dendrites. These are essentially needle-like extensions that can adversely impact a battery’s performance, lead to its sudden failure and, in most extreme cases, result in fires or explosions.