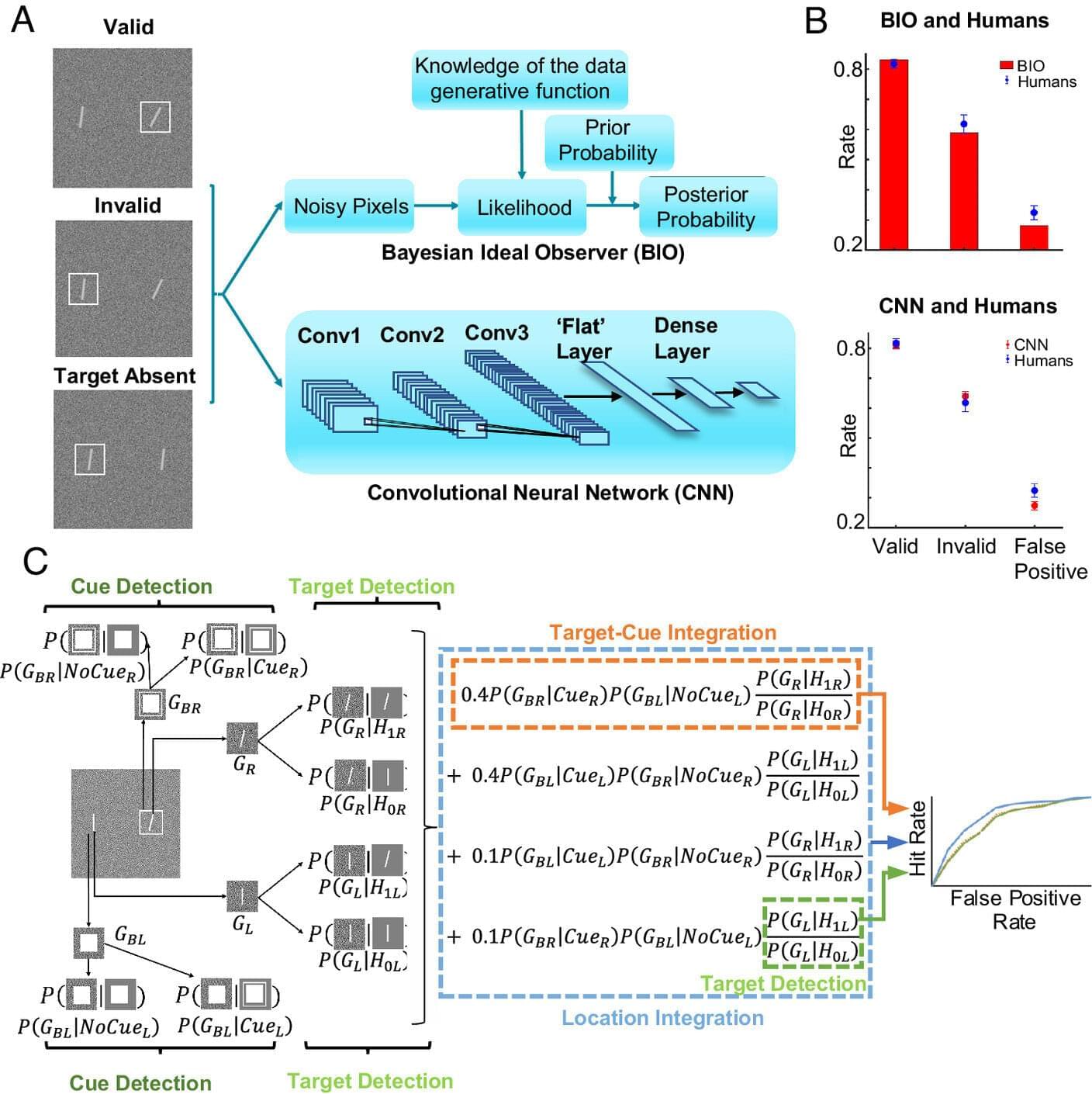
Shifting focus on a visual scene without moving our eyes—think driving, or reading a room for the reaction to your joke—is a behavior known as covert attention. We do it all the time, but little is known about its neurophysiological foundation.
Now, using convolutional neural networks (CNNs), UC Santa Barbara researchers Sudhanshu Srivastava, Miguel Eckstein and William Wang have uncovered the underpinnings of covert attention, and in the process, have found new, emergent neuron types, which they confirmed in real life using data from mouse brain studies.
“This is a clear case of AI advancing neuroscience, cognitive sciences and psychology,” said Srivastava, a former graduate student in the lab of Eckstein, now a postdoctoral researcher at UC San Diego.