A new CRISPR-powered light sensor can detect the faintest whispers of cancer in a single drop of blood.



Researchers demonstrated a broadband infrared frequency comb that can operate stably, efficiently, and accurately without the need for bulky external components. The device could be utilized in a remote sensor or portable mass spectrometer that can track and monitor multiple chemicals in real-time for extended periods.

Once considered an oddity of quantum physics, time crystals could be a good building block for accurate clocks and sensors, according to new calculations.

Researchers have fabricated a hair-thin microphone made entirely of silica fiber that can detect a large range of ultrasound frequencies beyond the reach of the human ear. Able to withstand temperatures up to 1,000°C, the device could eventually be used inside high-voltage transformers to detect early signs of failure before power outages occur.
“Conventional electronic sensors often fail under thermal stress or suffer from severe signal interference,” said Xiaobei Zhang, a member of the research team from Shanghai University. “Our all-fiber microphone can survive in hazardous environments and is completely immune to electromagnetic interference while remaining sensitive enough to hear the subtle early warning signals of equipment failure.”
In an article published in Optics Express, the researchers describe their new microphone, which is sensitive to frequencies from 40 kHz to 1.6 MHz. Unlike traditional microphones that rely on bulky housing, the new microphone is entirely integrated within a fiber just 125 microns in diameter.
It is not easy to follow the interactions of large molecules with water in real time. But this can be easier to hear than to see. This is how an international team deciphered the role of water in the collapse of PNIPAM.
Some polymers react to their environment with conformational changes: one of these is the polymer PNIPAM, short for poly(N-isopropylacrylamide). It is water-soluble below around 32 degrees Celsius, but above this temperature it precipitates and becomes hydrophobic. This qualifies it for smart sensor applications. But what actually happens between PNIPAM and the solvent water?
Researchers at Ruhr University Bochum, Germany, and the University of Illinois Urbana Champaign collaborated with sound production specialists from Symbolic Sound Corporation to investigate this question. Using sound representation, they were able to decipher the interaction of water molecules with PNIPAM for the first time. They reported their findings in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences on February 4, 2026.
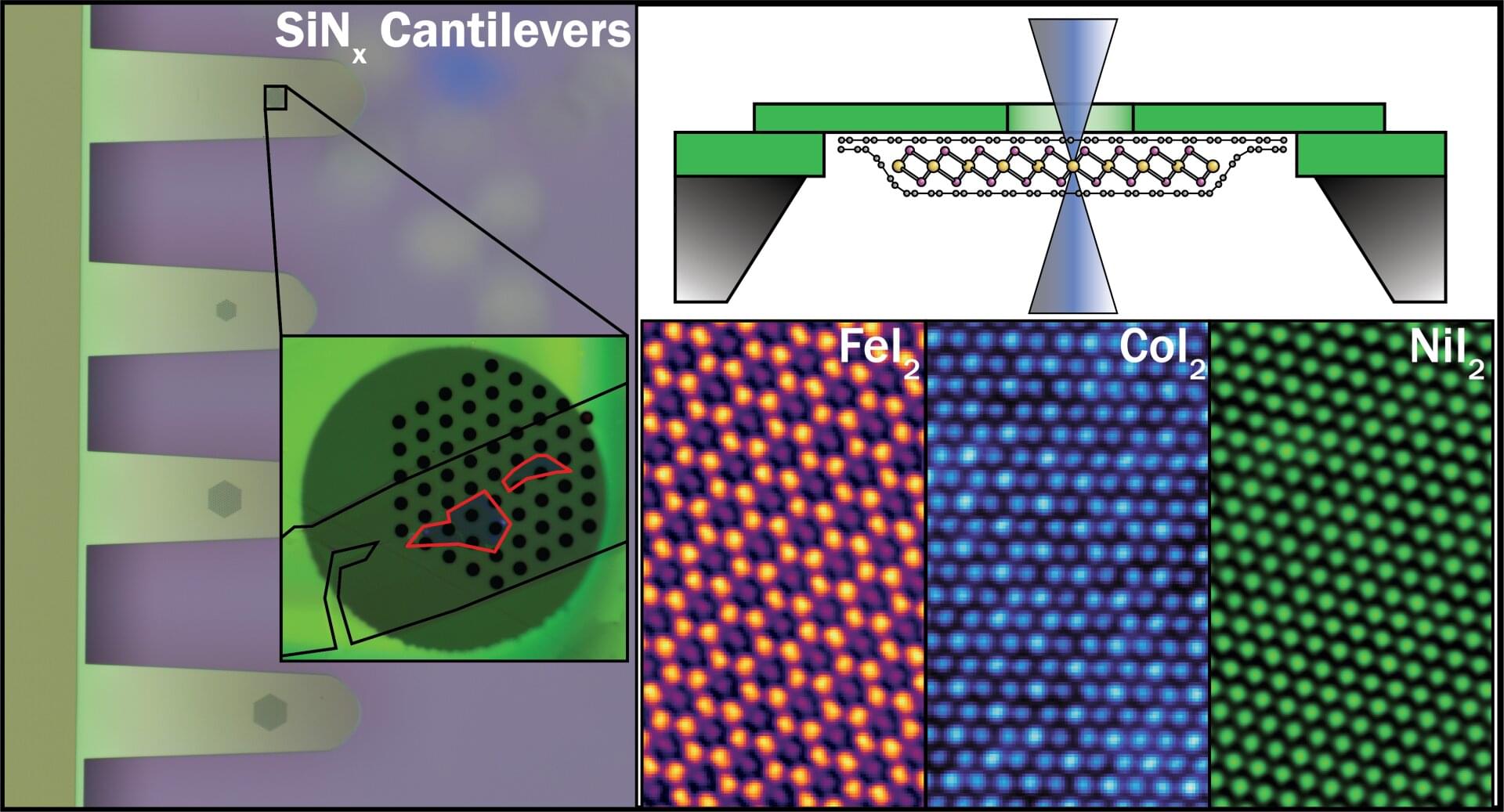
Two-dimensional (2D) materials promise revolutionary advances in electronics and photonics, but many of the most interesting candidates degrade within seconds of air exposure, making them nearly impossible to study or integrate into real-world technology. Transition metal dihalides represent a particularly compelling yet challenging class of materials, with predicted properties ideal for next-generation devices, but their extreme reactivity when exposed to air prevents even basic structural characterization.
Researchers at The University of Manchester’s National Graphene Institute have now achieved the first atomic-resolution imaging of monolayer transition metal diiodides, made possible by creating graphene-sealed TEM samples that prevent these highly reactive materials from degrading on contact with air.
The study, published in ACS Nano, demonstrates that fully encapsulating the crystals in graphene preserves atomically clean interfaces and extends their usable lifetime from seconds to months.

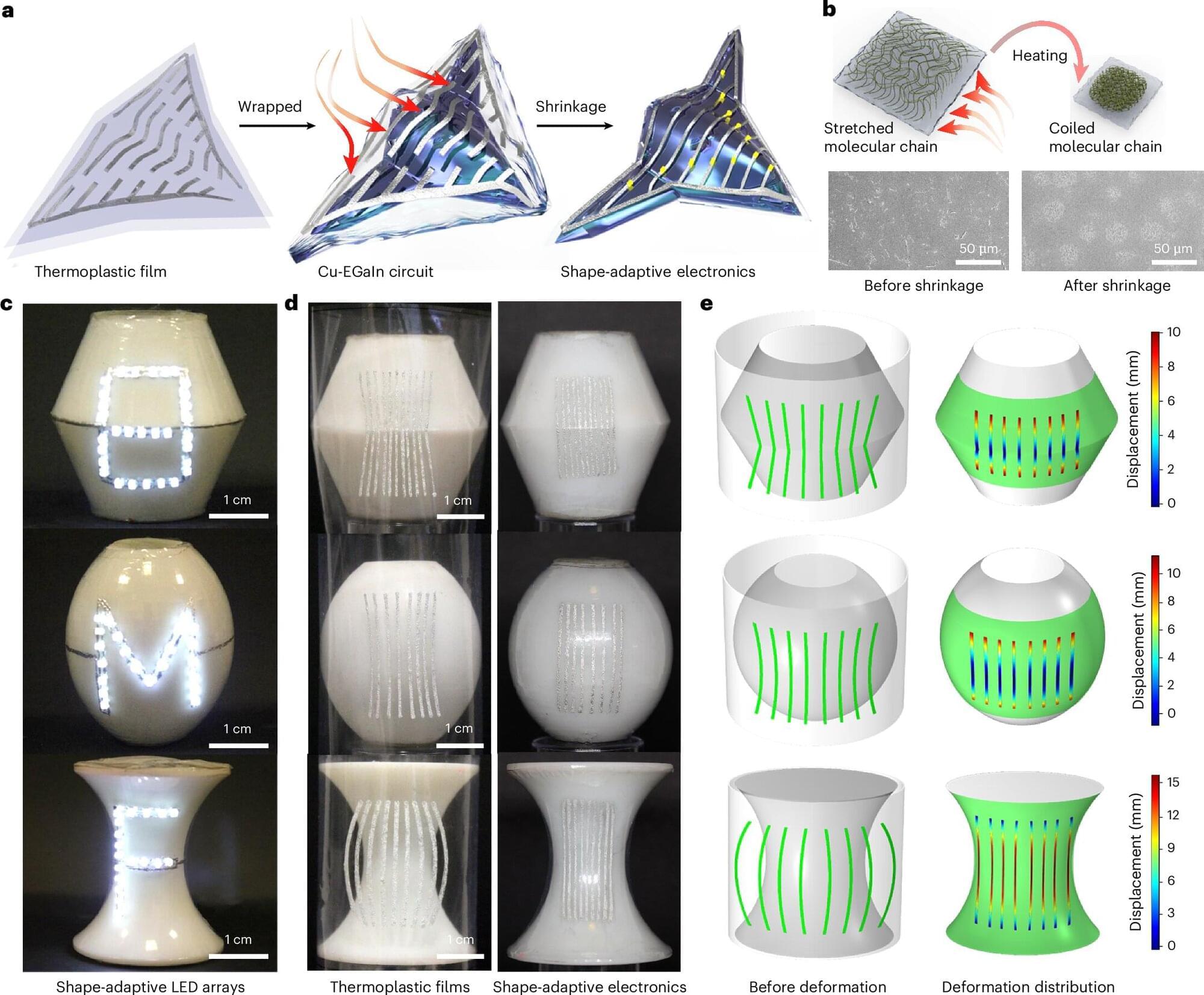
Most electronics are built on flat, stiff boards, which makes it incredibly difficult to fit them onto curved and irregular shapes we find in the real world, such as human limbs or curved aircraft wings. While flexible electronics have made some progress, they are often not durable enough or are too complex to manufacture for everyday use.

