Despite being a mature technology in existence for over several decades, silicon photonic modulators face scrutiny from industry and academic experts. In a recent editorial interview, experts emphasize the need to explore alternatives beyond the traditional platforms. The discussion centers on innovative modulator materials and configurations that could cater to emerging applications in data centers, artificial intelligence, quantum information processing, and LIDAR. Experts also outline the challenges that lie ahead in this field.
Optical and photonic modulators are technologically advanced devices that enable the manipulation of light properties—such as power and phase—based on input signals. Over the decades, scientists have researched and developed silicon photonic modulators with wide-ranging applications, including optical data communication, sensing, biomedical technologies, automotive systems, astronomy, aerospace, and artificial intelligence (AI).
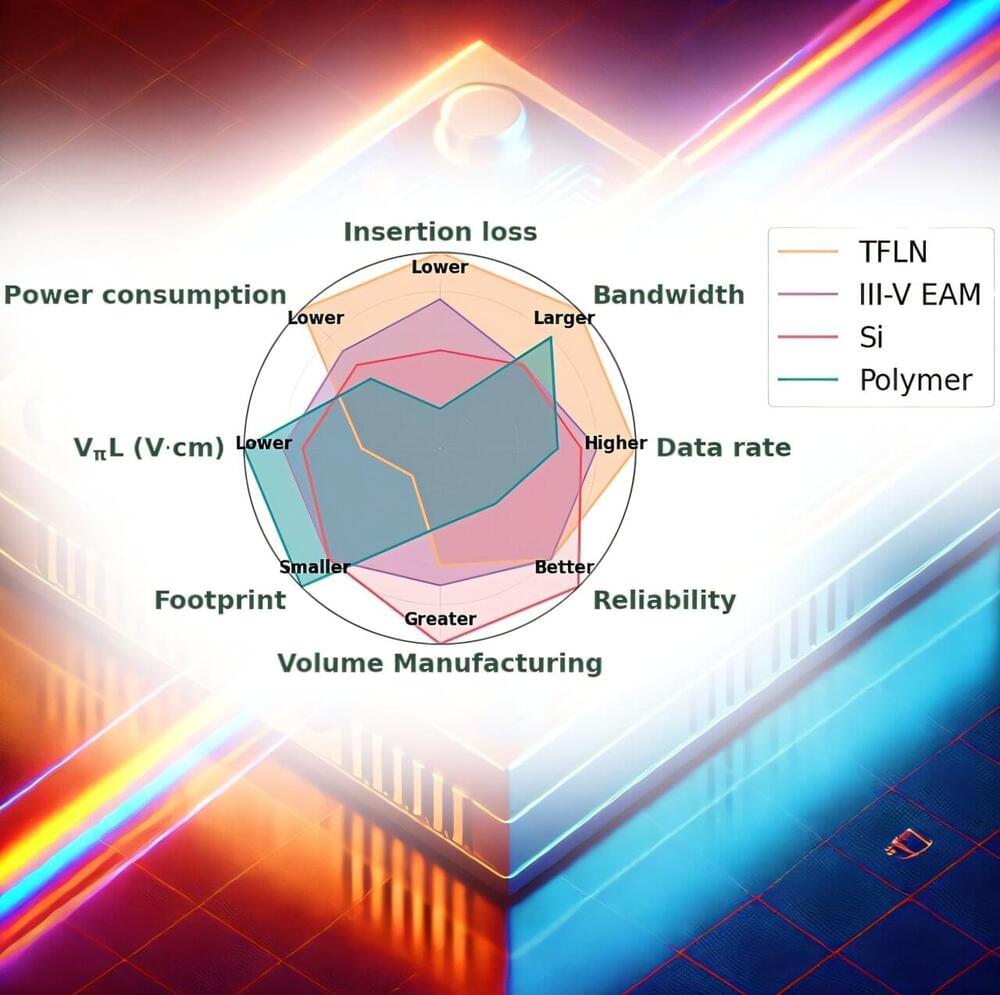
However, these modulators face bandwidth limitations and operational robustness issues stemming from the fundamental properties of silicon and other practical constraints, as highlighted by a panel of leading industry and academic experts in a recent editorial interview.