Researchers at the Buck Institute have extensively profiled the various inflammatory signals given off by senescent human cells and have generated a curated database available for use in the field.
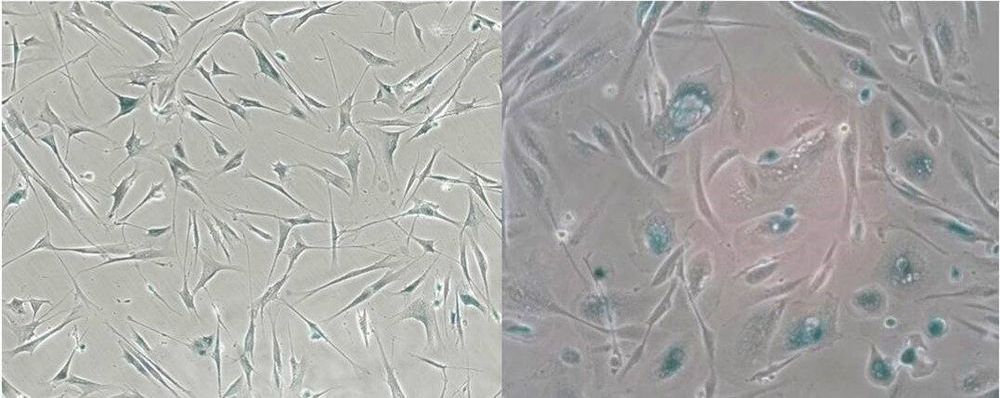
Senescent cells, which stop dividing under stress, are long- recognized drivers of multiple diseases of aging. Mouse studies have shown that targeted removal of these cells and the inflammatory factors they secrete, known as the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP), has beneficial results on multiple organ systems and functions. Success in the laboratory has given rise to companies and research projects aimed at developing either senolytics, drugs that clear senescent cells, or senomorphics, drugs that suppress the SASP. But drug development and clinical utilization require simple, reliable biomarkers to assess the abundance of senescent cells in human tissues. Publishing in PLOS Biology, researchers at the Buck Institute have extensively profiled the SASP of human cells and have generated a curated database available for use in the field.
“The stage is now set for the development of clinically-relevant biomarkers of aging,” said Judith Campisi, Ph.D., Buck professor and one of the senior authors on the paper. “This will speed efforts to get safe and effective drugs into the clinic and, in the long term, could enable physicians to give patients a clear read-out of how well, or poorly, their various tissues and organs are aging.”
Continue reading “Stage is set to develop clinically relevant, senescence-based biomarkers of aging” »