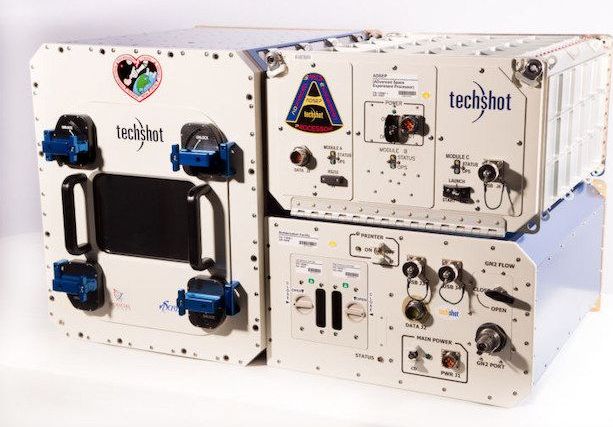
You might call it a giant leap for 3D bioprinting: Human heart cells have been 3D printed on the International Space Station (ISS) and are making their way back to Earth this week inside a SpaceX capsule. The 3D BioFabrication Facility (BFF) was developed by Techshot Inc., a commercial operator of microgravity research and manufacturing equipment, in partnership with nScrypt, a manufacturer of industrial 3D bioprinters and electronics printers.
“Our BFF has the potential to transform human healthcare in ways not previously possible,” said Techshot President and CEO John Vellinger.” We’re laying the foundation for an entire industry in space.”
If you’re wondering why they don’t just print the cells here on Earth, the answer is gravity. When attempting to print with soft, easily flowing biomaterials on Earth, the tissues collapse under their own weight, resulting in little more than a puddle, explained Techshot in a press release. “But when these same materials are used in the microgravity environment of space, the 3D-printed structures maintain their shapes.” The bio-ink used in the space station, consequently, did not contain the scaffolding materials or thickening agents normally required to resist the Earth’s gravitational pull.