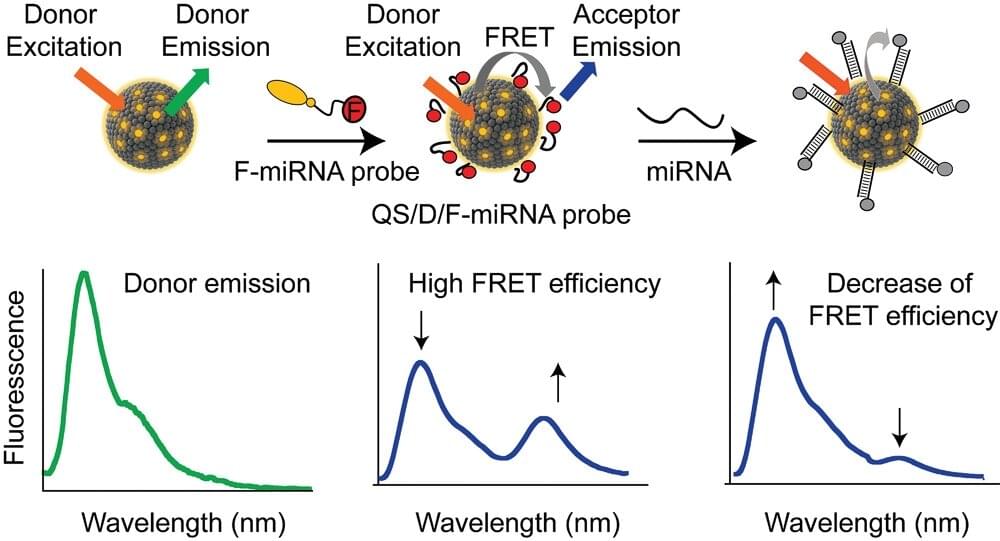
A new work by the Nanomol Group, belonging to the CIBER-BBN network, together with a team from the University of Rome Tor Vergata, presents new nanovesicles capable of crossing biological barriers such as cell membranes, while maintaining their sensing capacity, which makes them attractive probes for intracellular detection of biomarkers.
“The development of probes capable of sensing the biological environment and signaling the presence of a specific target molecule is a challenge with relevance in a variety of biomedical applications, from drug delivery to diagnostic tools,” says Mariana Köber, ICMAB researcher and corresponding author of the study, together with Nora Ventosa, from ICMAB, and Alessandro Porchetta, from the University of Rome Tor Vergata.
This work, which has been published in Advanced Functional Materials, presents the design of fluorescent nanovesicles functionalized with biomimetic DNA capable of translating their binding to a target molecule into an optical output, through a change in Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) and fluorescent emission.