Archive for the ‘particle physics’ category: Page 506
Feb 15, 2018
New form of light: Newly observed optical state could enable quantum computing with photons
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: computing, particle physics, quantum physics, weapons
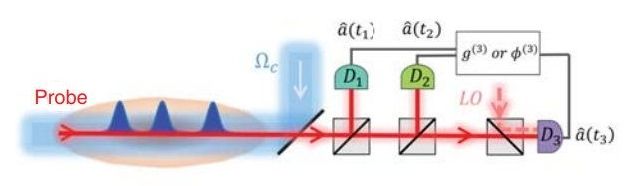
Try a quick experiment: Take two flashlights into a dark room and shine them so that their light beams cross. Notice anything peculiar? The rather anticlimactic answer is, probably not. That’s because the individual photons that make up light do not interact. Instead, they simply pass each other by, like indifferent spirits in the night.
But what if light particles could be made to interact, attracting and repelling each other like atoms in ordinary matter? One tantalizing, albeit sci-fi possibility: light sabers — beams of light that can pull and push on each other, making for dazzling, epic confrontations. Or, in a more likely scenario, two beams of light could meet and merge into one single, luminous stream.
It may seem like such optical behavior would require bending the rules of physics, but in fact, scientists at MIT, Harvard University, and elsewhere have now demonstrated that photons can indeed be made to interact — an accomplishment that could open a path toward using photons in quantum computing, if not in lightsabers.
Feb 14, 2018
Quantum computers ‘one step closer’
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: computing, particle physics, quantum physics
Quantum computing has taken a step forward with the development of a programmable quantum processor made with silicon.
The team used microwave energy to align two electron particles suspended in silicon, then used them to perform a set of test calculations.
By using silicon, the scientists hope that quantum computers will be more easy to control and manufacture.
Feb 14, 2018
Super Sensitive Sensor Sees What You Can’t
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: computing, particle physics
Engineers at Dartmouth College have developed a computer chip that can detect a single particle of light. Cameras with the chip would have visual abilities even a superhero would envy.
Feb 13, 2018
Picture of Single Trapped Atom Wins UK Science Photography Prize
Posted by Shane Hinshaw in categories: engineering, particle physics, science
Zoom in close on the center of the picture above, and you can spot something you perhaps never thought you’d be able to see: a single atom. Here is a close-up if, you’re having trouble:
This strontium atom is emitting light after being excited by a laser, and it’s the winner of the UK’s Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) photography award. The EPSRC announced the winners of its fifth annual contest yesterday. Winning photographer David Nadlinger, graduate student at the University of Oxford, was just excited to be able to show off his research.
“It’s exciting to find a picture that resonates with other people that shows what I spend my days and nights working on,” Nadlinger told me. The best part, to him, was “the opportunity to excite people about my research, more than winning a competition.”
Continue reading “Picture of Single Trapped Atom Wins UK Science Photography Prize” »
Feb 12, 2018
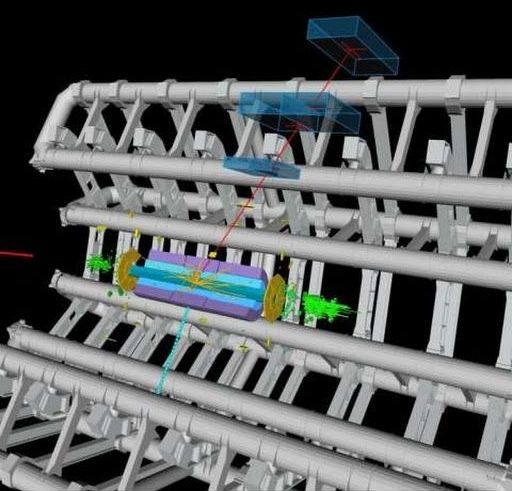
First high-precision measurement of the mass of the W boson at the LHC
Posted by Genevieve Klien in category: particle physics
Display of a candidate event for a W boson decaying into one muon and one neutrino from proton-proton collisions recorded by ATLAS with LHC stable beams at a collision energy of 7 TeV. (Image: CERN In a paper published today in the European Physical Journal C, the ATLAS Collaboration reports the first high-precision measurement at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) of the mass of the W boson. This is one of two elementary particles that mediate the weak interaction – one of the forces that govern the behaviour of matter in our universe. The reported result gives a value of 80370±19 MeV for th…
Feb 12, 2018
Light controls two-atom quantum computation
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: mathematics, particle physics, quantum physics
Scientists have demonstrated mathematical operations with a quantum gate between two trapped atoms that is mediated by photons.
Feb 11, 2018
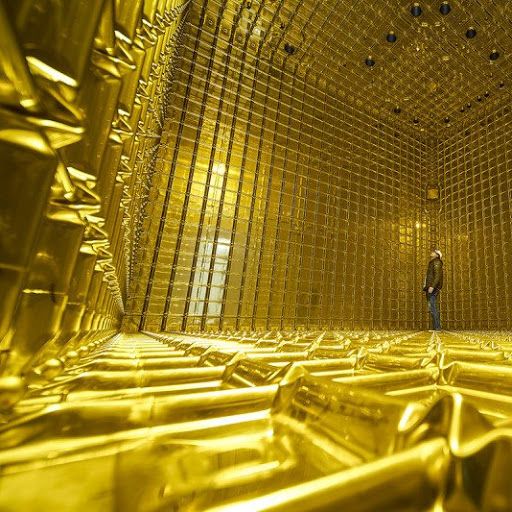
Peek inside a gilded cage of liquid argon made to spot neutrinos
Posted by Genevieve Klien in category: particle physics
This huge shiny cube is just a 1/20th scale model of the planned DUNE neutrino detector. It will be filled with liquid argon to catch these elusive particles.
Feb 11, 2018
Particle interactions on Titan support the search for new physics discoveries
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: nuclear energy, particle physics, supercomputing
Nuclear physicists are using the nation’s most powerful supercomputer, Titan, at the Oak Ridge Leadership Computing Facility to study particle interactions important to energy production in the sun and stars and to propel the search for new physics discoveries.
Feb 7, 2018
Fast-spinning spheres show nanoscale systems’ secrets
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in categories: nanotechnology, particle physics
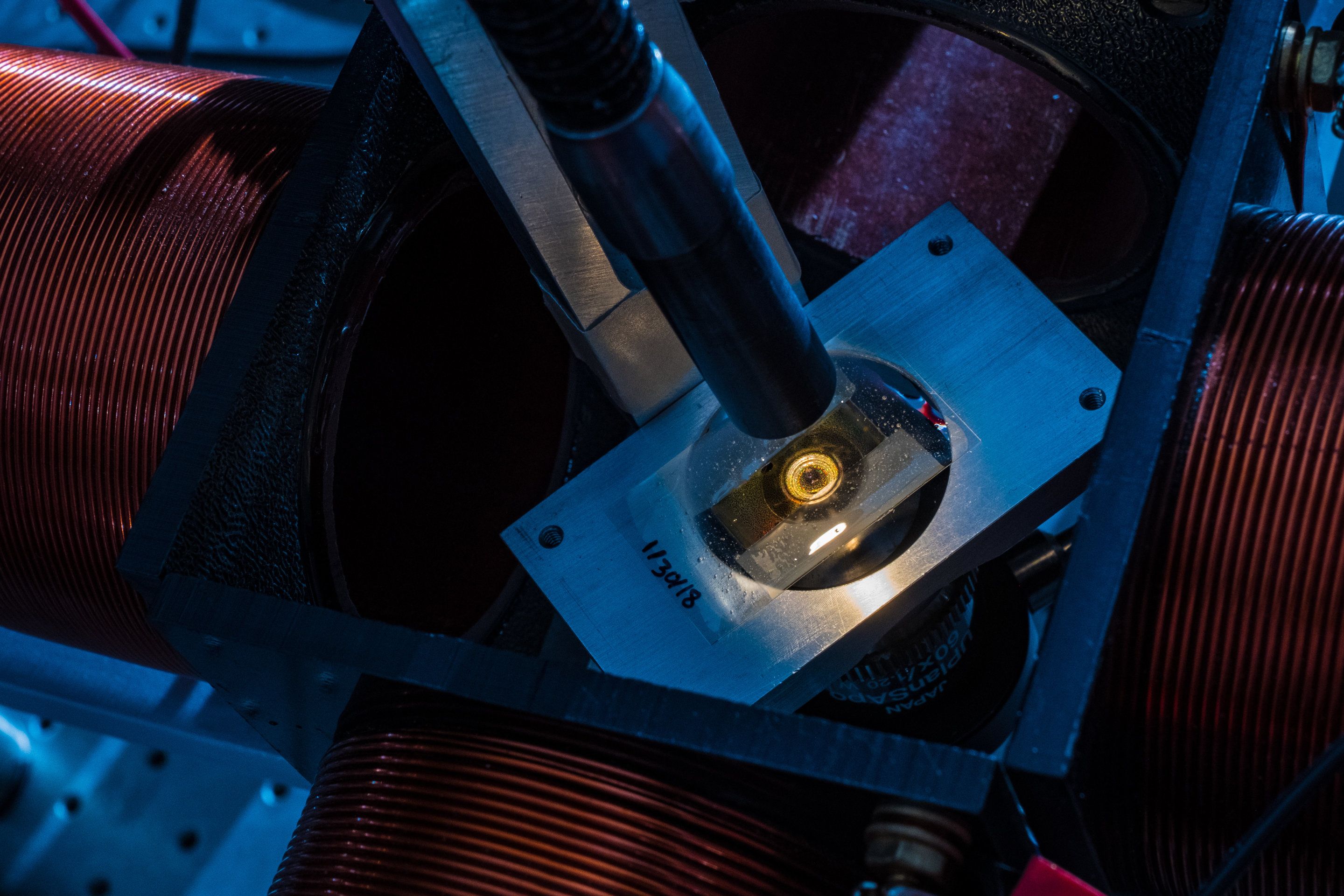
Spin a merry-go-round fast enough and the riders fly off in all directions. But the spinning particles in a Rice University lab do just the opposite.
Experiments in the Rice lab of chemical engineer Sibani Lisa Biswal show micron-sized spheres coming together under the influence of a rapidly spinning magnetic field. That’s no surprise because the particles themselves are magnetized.
Continue reading “Fast-spinning spheres show nanoscale systems’ secrets” »