Archive for the ‘neuroscience’ category: Page 879
Mar 13, 2017
Scientists get the green light to resurrect the dead with stem cells
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: biotech/medical, neuroscience
Bioquark, a biotech company based in the United States, has been given the go-ahead to begin research on 20 brain-dead patients, in an attempt to stimulate and regrow neurons and, literally, bring the patients back from the dead.
The technique is new and untested so the study will likely be controversial. By implanting stem cells in the patient’s brain, in addition to treating the spinal cord with infusions of chemicals and nerve stimulation techniques (both of which have been shown to bring people out of comas), they hope to reboot the brain and jump-start neural activity.
The result could be people coming back to life.
Mar 11, 2017
Hacking the Human Brain—New Tech Could Make It a Reality
Posted by Shane Hinshaw in categories: food, government, health, military, mobile phones, neuroscience
In Brief
- Your thoughts are your own, right? Perhaps not. New technology is bringing that day closer when the unscrupulous may actually be able to hack human thoughts.
- It raises a number of new ethical concerns for this brave new world we’re entering with each rotation of the Earth.
Everyone is familiar with the concept of hacking. It is why we all strive to protect our computers and smartphones from nefarious outside sources trying to break in to steal information, implant malware, etc. Hackers pose a threat to everyone from teenage smartphone users to the computer databases of government organizations. Hacking is a threat that we are all familiar with, and something that many know how to protect against. But, as the line between science and science fiction blurs, even hacking is getting a futuristic upgrade. Recently, at the Enigma Security Conference, University of Washington researcher and lecturer Tamara Bonaci revealed technology that could be used to essentially “hack” into people’s brains.
She created this technology around a game called Flappy Whale. While people played the game, the technology was able to covertly extract neural responses to subliminal imagery in the game like logos, restaurants, cars, etc. Now, hacking into people’s underlying feelings and thoughts about seeing a fast food restaurant doesn’t seem like it could cause much harm, but this technology has the potential to gather much more intimate information about a person like their religion, fears, prejudices, health, etc. This technology could evolve from an interesting way to understand human response to a military device. The possibilities range from an incredibly useful research tool to a potentially frightening interrogation device.
Continue reading “Hacking the Human Brain—New Tech Could Make It a Reality” »
Mar 6, 2017
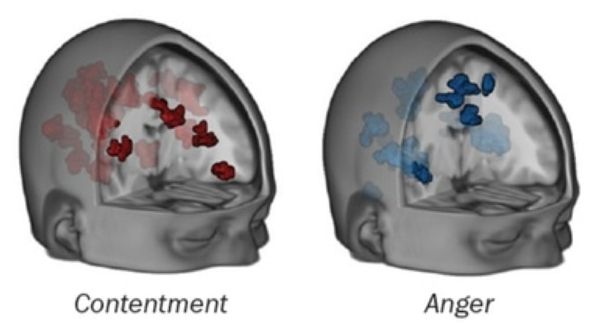
Can You Tell Someone’s Emotional State from an MRI?
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: biotech/medical, neuroscience
Mar 1, 2017
Intestinal bacteria alter gut and brain function
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in categories: biotech/medical, health, neuroscience
Research from McMaster University has found that bacteria in the gut impacts both intestinal and behavioural symptoms in patients suffering from irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), a finding which could lead to new microbiota-directed treatments.
The new study, published today in Science Translational Medicine, was led by researchers from the Farncombe Family Digestive Health Research Institute at McMaster, Drs. Premysl Bercik and Stephen Collins, in collaboration with researchers from the University of Waterloo.
IBS is the most common gastrointestinal disorder in the world. It affects the large intestine and patients suffer from abdominal pain and altered bowel habits like diarrhea and constipation, which are often accompanied by chronic anxiety or depression. Current treatments aimed at improving symptoms have limited efficacy because the underlying causes are unknown.
Continue reading “Intestinal bacteria alter gut and brain function” »
Feb 27, 2017
Science can help you reach enlightenment — but will it mess with your head?
Posted by Carse Peel in categories: government, neuroscience, science
A Navy SEAL, broad-chested and strongly built, floats peacefully on the water, as his recent deployment to a war-torn country becomes a distant memory.
Sealed inside a pitch-black sensory deprivation tank in the Mind Gym at Navy SEALs headquarters in Norfolk, Va., electrodes attached to his head, he has reached an altered state of consciousness referred to as “ecstasis” or “stepping outside oneself.”
It’s a state achieved by many others throughout time. High-performance athletes are in ecstasis when they ski down huge mountains or surf giant waves. Monks attain it after years of meditation. Mystics feel it when they have visions. And the US government uses it to try to reset their most elite warriors after brutal battles abroad.
Continue reading “Science can help you reach enlightenment -- but will it mess with your head?” »
Feb 27, 2017
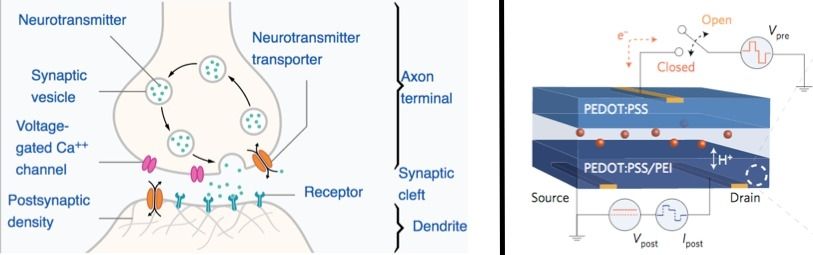
An ultra-low-power artificial synapse for neural-network computing
Posted by Sean Brazell in categories: computing, neuroscience
(Left) Illustration of a synapse in the brain connecting two neurons. (Right) Schematic of artificial synapse (ENODe), which functions as a transistor. It consists of two thin, flexible polymer films (black) with source, drain, and gate terminals, connected by an electrolyte of salty water that permits ions to cross. A voltage pulse applied to the “presynaptic” layer (top) alters the level of oxidation in the “postsynaptic layer” (bottom), triggering current flow between source and drain. (credit: Thomas Splettstoesser/CC and Yoeri van de Burgt et al./Nature Materials)
Stanford University and Sandia National Laboratories researchers have developed an organic artificial synapse based on a new memristor (resistive memory device) design that mimics the way synapses in the brain learn. The new artificial synapse could lead to computers that better recreate the way the human brain processes information. It could also one day directly interface with the human brain.
The new artificial synapse is an electrochemical neuromorphic organic device (dubbed “ENODe”) — a mixed ionic/electronic design that is fundamentally different from existing and other proposed resistive memory devices, which are limited by noise, required high write voltage, and other factors*, the researchers note in a paper published online Feb. 20 in Nature Materials.
Continue reading “An ultra-low-power artificial synapse for neural-network computing” »
Feb 27, 2017
‘They want to be literally machines’: Writer Mark O’Connell on the rise of transhumanists
Posted by Zoltan Istvan in categories: biotech/medical, cryonics, cyborgs, life extension, neuroscience, transhumanism
Slate book columnist Mark O’Connell’s new book To Be a Machine, which is specifically about #transhumanism, is out tomorrow. So there’s a ton of reviews out in major media. The last chapter in the book is about my work. Here are 3 reviews just out on the book. ALSO, I highly encourage you to BUY the book to help transhumanism grow. Mark’s book is the first book specifically on the movement with this kind of international attention, and the better the book does the first week, the more people will know about transhumanism: http://www.theverge.com/2017/2/25/14730958/transhumanism-mar…biohackers &
http://www.theglobeandmail.com/arts/books-and-media/book-rev…e34127614/ &
http://www.themillions.com/2017/02/mark-oconnell-doesnt-want…rview.html
Feb 26, 2017
10 Dangerous Brain-Damaging Habits to Stop Immediately
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: biotech/medical, food, neuroscience
Need a new excuse for not working too late and or studying to hard well you have one as it can create brain damage.
The only organ in our body that ‘thinks’ is often the one we think the least about.
Our brain is the single most important organ in our body, controlling everything we do, from breathing, walking, eating, sleeping, etc. It’s the central processor for all our bodily functions, the part that interprets what we see and hear, smell and taste, and even a place where the chemical reaction associated with love occurs.
Continue reading “10 Dangerous Brain-Damaging Habits to Stop Immediately” »
Feb 26, 2017
The human brain makes fructose, researchers discover – here’s why that might be a big deal
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: biotech/medical, food, neuroscience
Researchers at Yale University have discovered that the brain is capable of making fructose – a simple sugar, usually found in fruit, vegetables and honey.
Not all sugars are equal. Glucose is a simple sugar that provides energy for the cells in your body. Fructose has a less important physiological role and has been repeatedly linked to the development of obesity and type 2 diabetes. When there is excess glucose the processes that break it down can become saturated, so the body converts glucose into fructose instead, using a process known as the “polyol pathway”, a chemical reaction involved in diabetic complications. The researchers at Yale reported in the journal, JCI Insight, that the brain uses the polyol pathway to produce fructose in the brain.