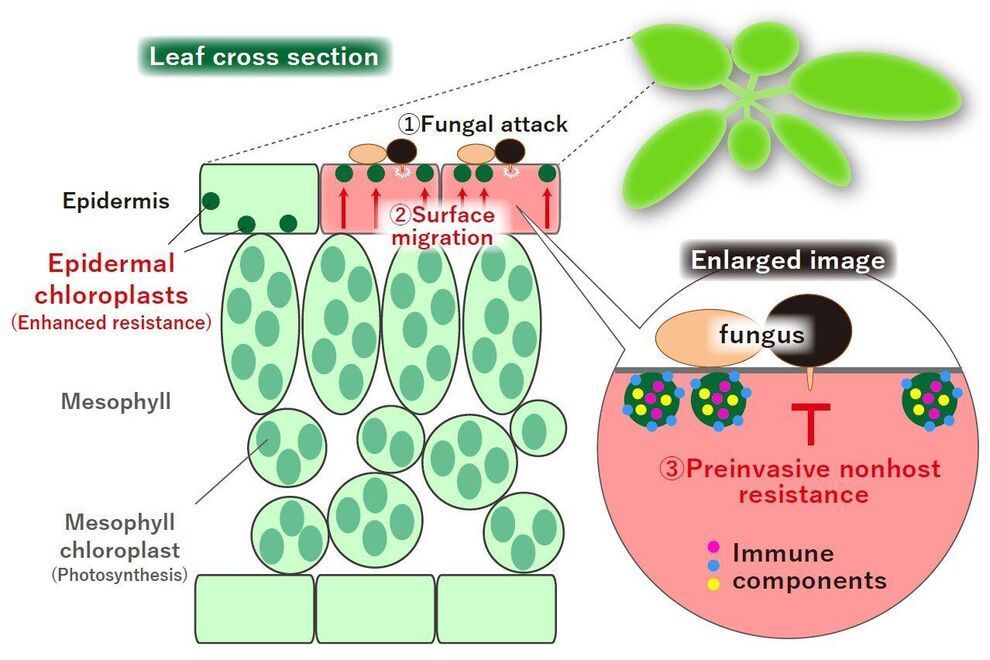
It is said that 10 to 15% of the world’s agricultural production loss is caused by diseases, which is equivalent of the food for about 500 million people. And since 70–80% of this plant disease is caused by filamentous fungi, protecting crops from filamentous fungi is an important issue in effectively feeding the world population. In order for pathogenic fungi to infect plants, they must break through the epidermal cells of the plant and invade the interior. In other words, plant epidermal cells act as the first barrier to stop the attack of pathogenic fungi in the environment. So what kind of defense functions do epidermal cells have?
Interestingly, it was known that the epidermis of plants contain small chloroplasts that are not so involved in photosynthesis. However, it was unclear what function it had. Why are there small chloroplasts in the epidermis of plants that do not contribute much to photosynthesis?
Assistant Professor Hiroki Irieda of the Faculty of Agriculture, Shinshu University and Professor Yoshitaka Takano, Graduate School of Agriculture, Kyoto University, found that small chloroplasts in the epidermis of plants control the entry of fungal pathogens. The duo discovered that the small chloroplasts move inside the cell dramatically to the surface layer in response to the fungal attack and is involved in such defense response. Furthermore, the duo found that multiple immune factors involved in the defense response of plants are specifically found in the epidermal chloroplast, which contributes to the enhancement of resistance to the invasion of pathogen filamentous fungi.