Apr 24, 2020
Highly quaternized polystyrene ionomers for high performance anion exchange membrane water electrolysers
Posted by Fyodor Rouge in categories: evolution, futurism
Water spliting got cheaper.
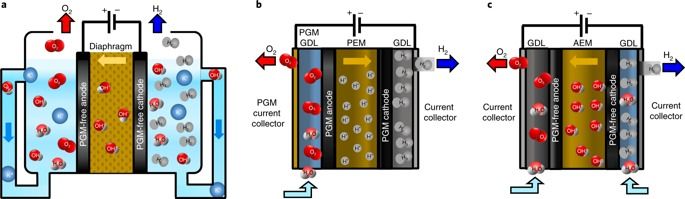
Alkaline anion exchange membrane (AEM) electrolysers to produce hydrogen from water are still at an early stage of development, and their performance is far lower than that of systems based on proton exchange membranes. Here, we report an ammonium-enriched anion exchange ionomer that improves the performance of an AEM electrolyser to levels approaching that of state-of-the-art proton exchange membrane electrolysers. Using rotating-disk electrode experiments, we show that a high pH (13) in the electrode binder is the critical factor for improving the activity of the hydrogen- and oxygen-evolution reactions in AEM electrolysers. Based on this observation, we prepared and tested several quaternized polystyrene electrode binders in an AEM electrolyser. Using the binder with the highest ionic concentration and a NiFe oxygen evolution catalyst, we demonstrated performance of 2.7 A cm−2 at 1.8 V without a corrosive circulating alkaline solution. The limited durability of the AEM electrolyser remains a challenge to be addressed in the future.