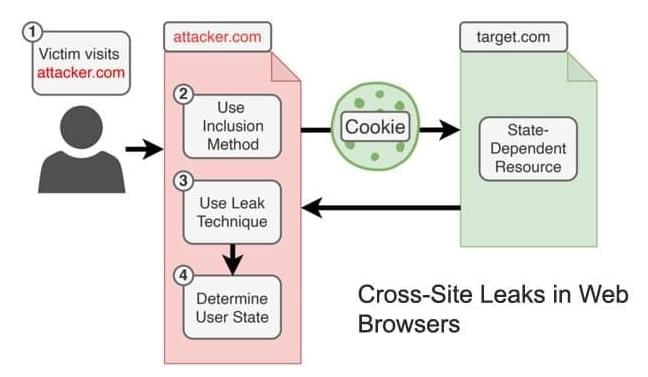
Researchers have discovered 14 new types of cross-site data leakage attacks against a number of modern web browsers, including Tor Browser, Mozilla Firefox, Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Apple Safari, and Opera, among others.
Collectively known as “XS-Leaks,” the browser bugs enable a malicious website to harvest personal data from its visitors as they interact with other websites in the background without the targets’ knowledge. The findings are the result of a comprehensive study of cross-site attacks undertaken by a group of academics from Ruhr-Universität Bochum (RUB) and Niederrhein University.
“XS-Leaks bypass the so-called same-origin policy, one of a browser’s main defences against various types of attacks,” the researchers said in a statement. “The purpose of the same-origin policy is to prevent information from being stolen from a trusted website. In the case of XS-Leaks, attackers can nevertheless recognize individual, small details of a website. If these details are tied to personal data, those data can be leaked.”