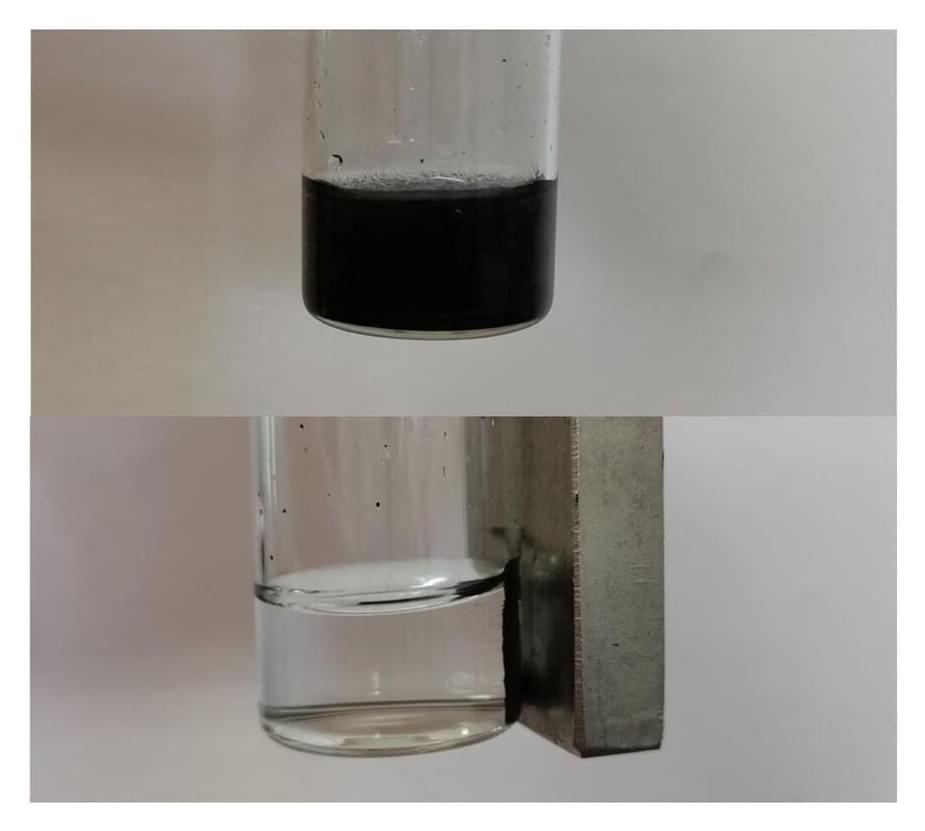
Membrane filters don’t require much energy to purify water, making them popular for wastewater treatment. To keep these materials in tip-top condition, they’re commonly cleaned with large amounts of strong chemicals, but some of these agents destroy the membranes in the process. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces have developed reusable nanoparticle catalysts that incorporate glucose to help efficiently break down contaminants inside these filters without damaging them.
Typically, dirty wastewater filters are unclogged with strong acids, bases or oxidants. Chlorine-containing oxidants such as bleach can break down the most stubborn organic debris. But they also damage polyamide membranes, which are in most commercial nanofiltration systems, and they produce toxic byproducts. A milder alternative to bleach is hydrogen peroxide, but it decomposes contaminants slowly.
Previously, scientists have combined hydrogen peroxide with iron oxide to form hydroxyl radicals that improve hydrogen peroxide’s efficiency in a process known as the Fenton reaction. Yet in order for the Fenton reaction to clean filters, extra hydrogen peroxide and acid are needed, increasing financial and environmental costs. One way to avoid these additional chemicals is to use the enzyme glucose oxidase, which simultaneously forms hydrogen peroxide and gluconic acid from glucose and oxygen. So, Jianquan Luo and colleagues wanted to combine glucose oxidase and iron oxide nanoparticles into a system that catalyzes the Fenton-based breakdown of contaminants, creating an efficient and delicate cleaning system for membrane filters.