Mar 17, 2022
Ultrahard chiton teeth discovery offers clues to next-generation advanced materials
Posted by Dan Breeden in categories: energy, engineering, food
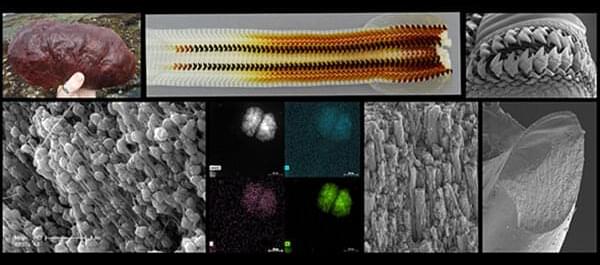
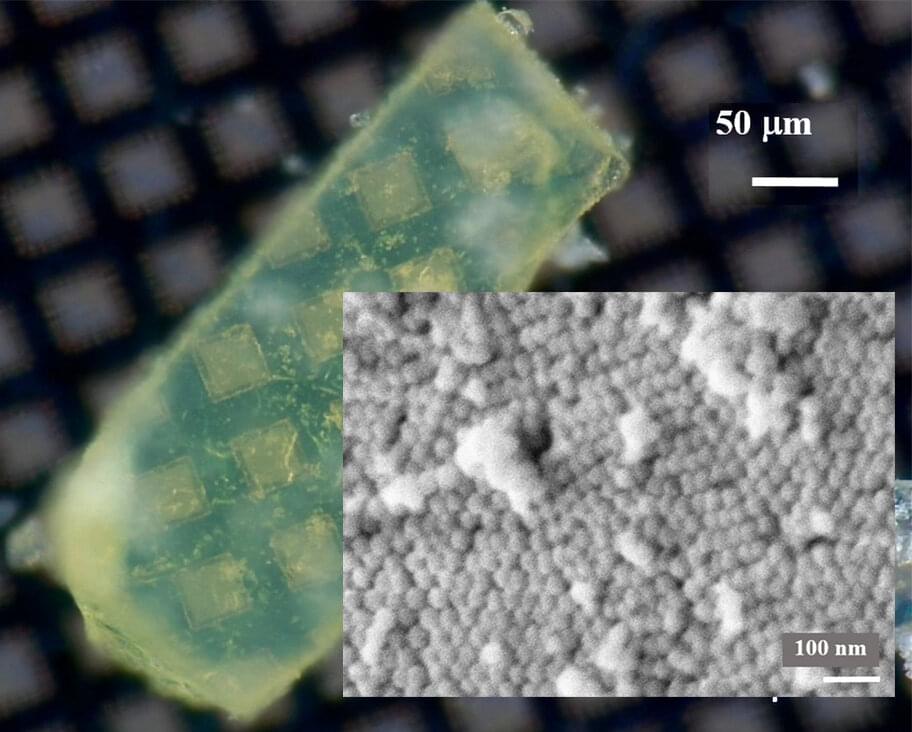
The teeth of a mollusk can not only capture and chew food to nurture its body, but the marine choppers also hold insights into creating advanced, lower-cost and environmentally friendly materials.
David Kisailus, UC Irvine professor, and graduate student Taifeng Wang, both in materials science and engineering, took a close look at the ultrahard teeth of the Northern Pacific Cryptochiton stelleri or gumboot chiton. Their findings are published in the Small Structures April 2022 issue.
“The findings in our work are critical, as it not only provides an understanding of the precision of natural systems in mineralization to form high-performance architected materials, but also provides insights into bioinspired synthetic pathways to a new generation of advanced materials in a broad range of applications from wear-resistant materials to energy storage systems,” said Kisailus.