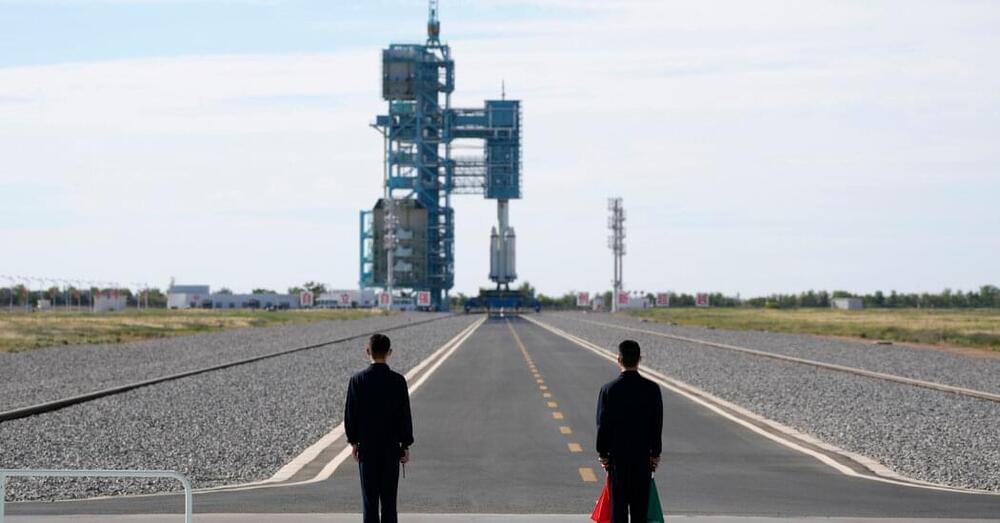
While grand spaceflight plans of some nations have ended up many years behind schedule, China completed the assembly in orbit of its Tiangong space station in late October, only 22 months later than planned. And on Nov. 29, the Shenzhou 15 mission blasted off from China’s Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center deep in the Gobi Desert and took three astronauts to the space station to begin permanent occupancy of the outpost.
These human spaceflight achievements, combined with recent space probes to the moon and Mars, add to the evidence that China is running a steady space marathon rather than competing in a head-to-head space race with the United States. That China’s space program is making good time toward its long-term goals was reinforced during a rare visit for foreign media to the country’s heavily guarded desert rocket base for the Nov. 29 launch — including lengthy interviews with senior Chinese space officials by in for The New York Times.