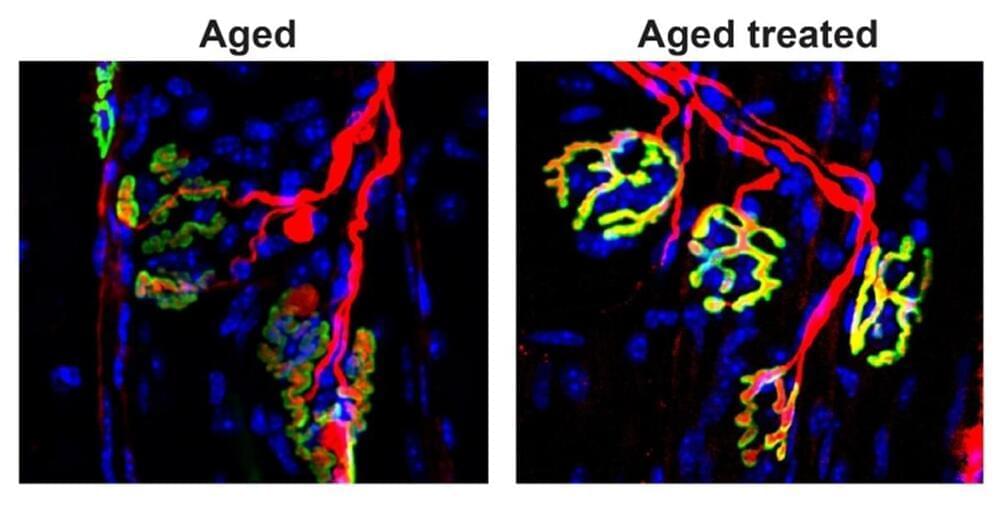
Scientists from the University of California Davis (UC Davis) Comprehensive Cancer Center have recently published in Cell Death and Disease, identifying a critical protein that causes cells to die. The protein is described as an epitope, which is a section of the protein that is recognized by the immune system to activate a response. This epitope was distinctly found on the CD95 receptor, known to trigger programmed cell death. The report demonstrates a new mechanism to trigger cell death and provide further insight into improved disease treatments.
CD95 receptors, also referred to a “Fas”, are cell death receptors which are present on cell membranes. Once Fas is activated, it generates a signaling cascade which elicits cell death. The mechanism by which cells self-destruct has been an important research topic. By understanding cell death, scientists can generate better therapies for different diseases, including cancer.
Currently, cancer is treated by surgery, chemotherapy, or radiotherapy. Despite initial success, these treatments are unable to fully eradicate tumor cells. Immunotherapy is a new approach to target cancer. Immunotherapy refers to therapeutics modulating the immune system to elicit an effective immune response. This is a more indirect approach compared to lysing tumors with a chemical. One specific immunotherapy referred to as chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy is a treatment in which T cells, or cytotoxic immune cells, are engineered to lyse tumor cells. Unfortunately, CAR T-cell therapy is limited due to the tumor’s ability to prevent T cell activation.