Mar 21, 2016
Treating disease at stage zero
Posted by Klaus Baldauf in categories: bioengineering, biotech/medical, health, information science, nanotechnology
It sounds really obvious, but hospitals aren’t for healthy people. The world’s entire health system is really there to react once people get ill. If doctors are able to catch an illness at stage one that’s great, but if it reaches stage three or four there’s often not that much that can be done. So what if we could treat patients at stage zero and predict the likelihood of contracting diseases? We could then get treatment to people who need it much earlier and take preventative steps to avoid illness altogether.
Currently, when we think of monitoring in healthcare we’re usually referring to monitoring patients’ reactions to drugs or treatments, but this is changing. No amateur runner’s uniform is complete these days without a Fitbit or some kind of analytics tool to monitor progress, so the idea of monitoring the healthy is becoming ingrained in the public’s consciousness. But Fitbits only scrape the surface of what we can do. What if the data from fitness trackers could be combined with medical records, census data and the details of supermarket loyalty cards to predict the likelihood of contracting a particular disease?
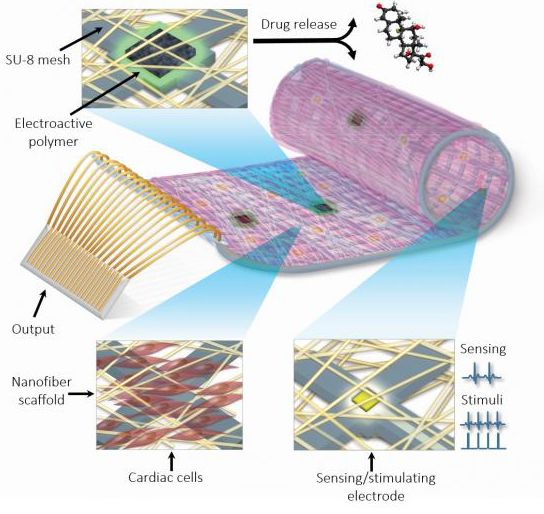
With big data we can move from reacting to predicting, but how do we move beyond just making predictions; how do we prevent disease from occurring altogether? Up until now all of our monitoring technology has been located outside of the body, but nano-sized entities made of DNA could one day patrol the body, only acting when they come into contact with specific cells – cancer cells, for example. The technology that would turn tiny machines – roughly the size of a virus – into molecular delivery trucks that transport medication is already being worked on by bioengineers. If this kind of technology can be used to treat cancer, without needing to release toxic agents into the body, can the same technology be inserted into a healthy person and lie in wait for the opportunity to fight disease on its host’s behalf?