Archive for the ‘food’ category: Page 300
Oct 6, 2016
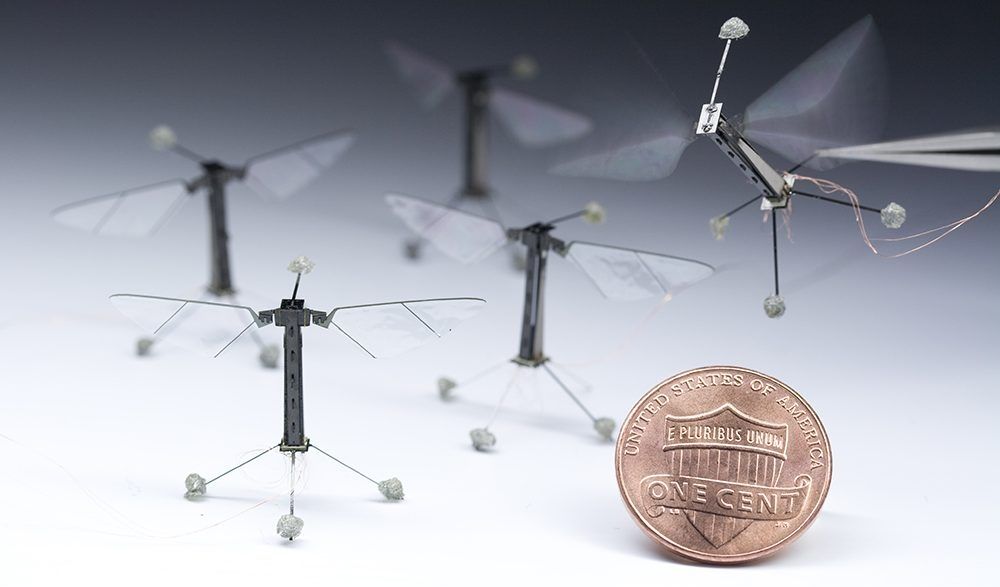
Project Originally Funded By DARPA Seeks To Replace Bees With Tiny, Winged Robots
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: drones, food, information science, internet, military, mobile phones, robotics/AI, transhumanism
Got a bee shortage? No problem, DARPA has you covered.
Following the news that the honeybee is now officially an endangered species as “colony collapse disorder” accelerates, it seems that a Harvard research team has the solution – robotic honeybees. Instead of attempting to save the bees by reducing the use of pesticides or revising safety standards for cell phone radiation, the focus has shifted to replacing the bees altogether. Harvard University researchers, led by engineering professor Robert Wood have been tweaking “RoboBees” since their initial introduction in 2009. The bee-sized robots made of titanium and plastic represent a breakthrough in the field of micro-aerial vehicles. The size of the components needed to create flying robots were previously too heavy to make a such a small structure lightweight enough to achieve flight. Current models weigh only 80 mg and have been fitted with sensors that detect light and wind velocity.
Researchers claim that the bees could artificially pollinate entire fields of crops and will soon be able to be programmed to live in an artificial hive, coordinate algorithms and communicate among themselves about methods of pollination and the locations of particular crops. In addition, RoboBees have been suggested for other uses including searching disaster sites for survivors, monitoring traffic, and “military and police applications.” These applications could include using RoboBees to “scout for insurgents” on battlefields abroad or allowing police and SWAT teams to use the micro-robots to gather footage inside buildings.
Oct 5, 2016
Food production in a world without meat — By Mbali Kgame | Design Indaba
Posted by Odette Bohr Dienel in categories: environmental, ethics, food, futurism

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cimOBpVMLxU
“Meat production is detrimental to the environment and at the high rate at which it is consumed, it can also increase the risk of colorectal cancer by 18 per cent. This is according to a review of 800 studies conducted by the World Health Organisation (WHO).”
Oct 2, 2016
Dark Future Ahead 18 – News from the ‘Net of a Cyberpunk bent
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: biotech/medical, food, mobile phones
Still keeping my optics working looking for news to apply to your cyberpunk games and writings.
A way to defend against counterfeit drugs and maybe food too, miniature edible barcodes. Inexpensive, practical and readable with a slight modification of a smart phone.
For some reason, the idea of edible food wrappers just seems very cyberpunk to me. Full of advertising and nutrition!
Sep 29, 2016
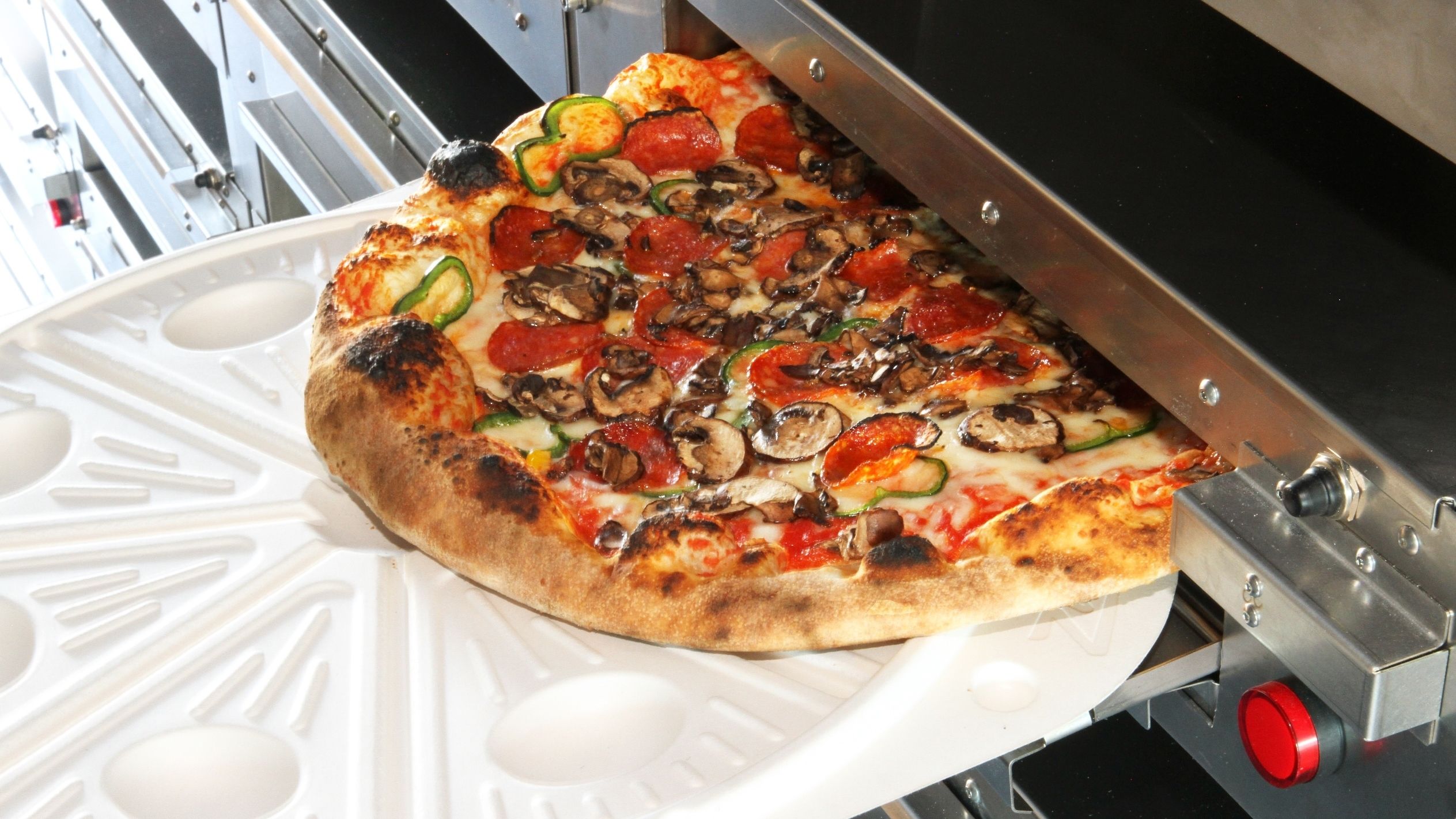
Our Robot Overlords Are Now Delivering Pizza, And Cooking It On The Go
Posted by Shane Hinshaw in categories: food, robotics/AI
A Silicon Valley start-up wants to use technology to solve the pizza paradox. It’s a food that’s meant to be delivered, but never tastes quite as good upon arrival.
Sep 29, 2016
Fund Medical Research to End Age-Related Disease
Posted by Steve Hill in categories: biotech/medical, food, health, life extension, transportation
Please sign this petition to the NIH to help get more funding for aging research.
Every year about two million Americans die of illnesses doctors cannot cure. Cancer afflicts 50% of men and 30% of women. Five hundred and ninety five thousand Americans will die of cancer this year. Millions get heart diseases, strokes, etc. Every year 1,612,552 Americans die of the top 8 illnesses that doctors are unable to cure. Over a 30-year period, 48,376,560 United States citizens will die of the top 8 illnesses. Let us not forget other disabling and potentially curable illnesses. How much is it worth to save them? We have the resources and opportunity to cure age-related disease.
History has shown that medical research actually saves money. We now spend three trillion two hundred billion dollars yearly for health care. The health care expenditures will increase as our population grows with more senior citizens.
Continue reading “Fund Medical Research to End Age-Related Disease” »
Sep 26, 2016
Plans for Belarusian-Russian laser technology R&D center
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: food, materials
The new Belarusian-Russian R&D center for laser technologies is supposed to open in Minsk. The center will take care of the most important and new practical applications of laser technologies, said Sergei Bagayev. The scope of research will vary from agricultural applications to using lasers for the advanced processing of oil products to get modern materials.
Sep 24, 2016
Bioengineered bacteria could be used to 3D print food, medicine, and tools on Mars
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: 3D printing, bioengineering, biotech/medical, food, solar power, space travel, sustainability
Just like checking your bag on a commercial airline, space travel comes with some pretty big weight restrictions. How big? According to estimates, reaching space costs a whopping $10,000 per pound, which means that every ounce saved has a big impact on the bottom line.
That’s where a group of Danish researchers comes in. The team is working on a synthetic biology project called CosmoCrops, which hopes to use bacteria to make it possible to 3D print everything needed for a respectable space mission, using a cutting-edge co-culturing system. And it could even make life better for those of us back on Earth in the process.
“We are trying to make space exploration cheaper, because many inventions we use in our daily life were invented because of space exploration, like Velcro and solar energy,” Joachim Larsen, one of the students working on the project, told Digital Trends. “The way we want to achieve this is to [be] able to produce everything from food to medicine and bioplastic for 3D printers out in space — making the space rocket a lot lighter.”
Sep 23, 2016
The Next Step for Veganism Is Ditching Our Bodies and Digitizing Our Minds
Posted by Zoltan Istvan in categories: biological, cyborgs, food, life extension, transhumanism
Connecting the dots between transhumanism, veganism, and caring for animals. My new story for Vice Motherboard:
The answer is bewildering—and it probably won’t be satisfying to plant-loving people. Nonetheless, it will inevitably eliminate most human-caused animal deaths. The answer is transhumanism—the movement that aims to replace human biology with synthetic and machine parts.
You see, the most important goal of transhumanism is to try to overcome death with science and technology. Most cellular degeneration—otherwise known as aging and sickness—comes from the failing of cells. That failure is at least partially caused by the daily act of eating and drinking—of putting foreign objects into our bodies which cells have to consume or discard to try to create energy. Paraxdocially, it’s stressful and hard work for cells to endlessly do this just to live. A simple way to eliminate this Sisyphean task—all the steaks, chocolate donuts, bacon breakfasts, and even my favorite, scotch—is to get rid of human reliance on food and drink entirely.
Continue reading “The Next Step for Veganism Is Ditching Our Bodies and Digitizing Our Minds” »
Sep 20, 2016
4D Printing: Shaping The Future of Solar Cells
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: 3D printing, 4D printing, food, solar power, sustainability
Definitely many benefits to 4D including manufacturing, tech devices, and energy.
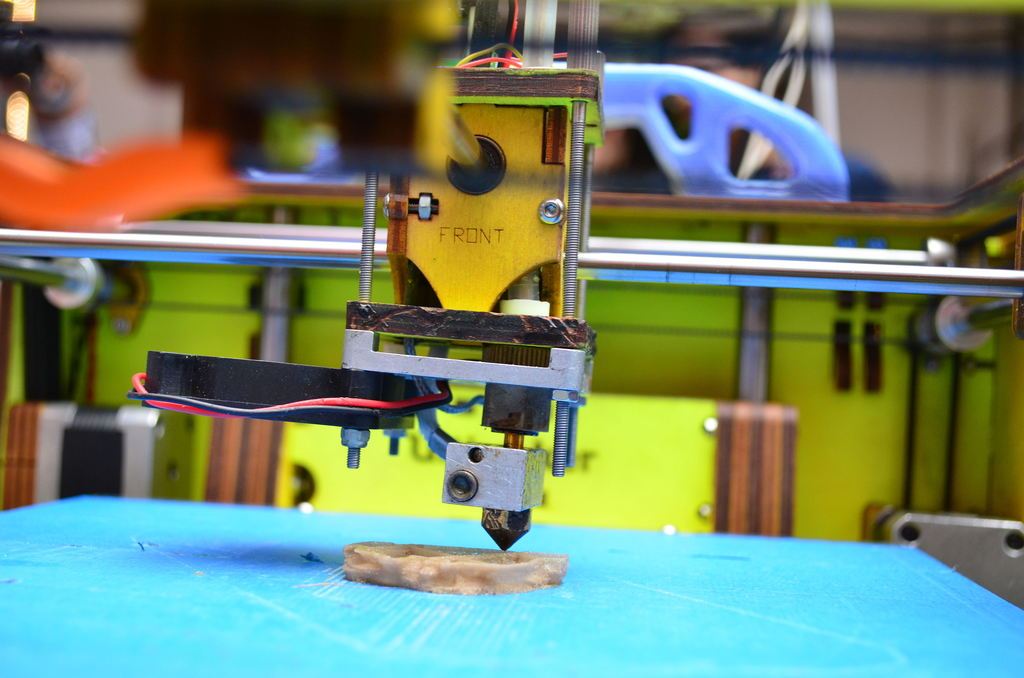

A team of researchers has uncovered the key to what they call 4D printing – and solar energy may be one of the top 2 fields to benefit from the great invention.
Continue reading “4D Printing: Shaping The Future of Solar Cells” »