Jan 1, 2023
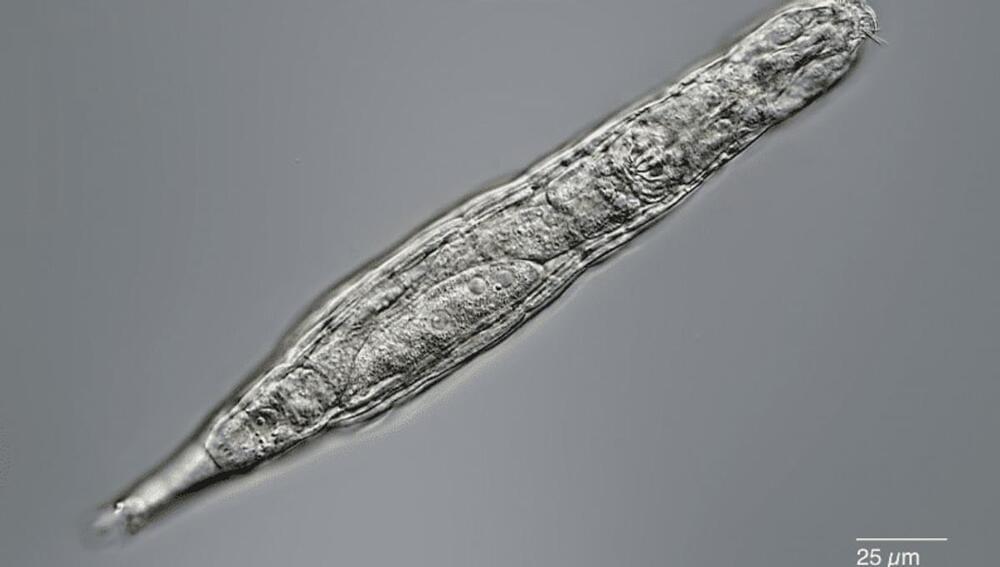
Microscopic Animal Brought Back To Life After 24,000 Years Frozen In Siberian Permafrost
Posted by Dan Breeden in categories: biological, chemistry, life extension
Tardigrades have competition in the realm of microscopic and incredibly sturdy beasties. Like tardigrades, Bdelloid rotifers can also survive drying, freezing, starving, and even low-oxygen conditions. Now, scientists report that they revived some of these rotifers after having been frozen in Siberian permafrost for at least 24,000 years.
The incredible observations are reported in the journal Current Biology. The researchers took samples of permafrost about 3.5 meters (11.5 feet) deep and slowly warmed the sample, which led to the resurrection of several microscopic organisms including these tiny little animals.
“Our report is the hardest proof as of today that multicellular animals could withstand tens of thousands of years in cryptobiosis, the state of almost completely arrested metabolism,” co-author Stas Malavin of the Soil Cryology Laboratory at the Institute of Physicochemical and Biological Problems in Soil Science in Pushchino, Russia, said in a statement.