But astronomer Tiger Hsiao of National Tsing Hua University says we might be looking for the wrong thing. In a new study, he and colleagues set out to calculate whether it would also be possible to use a Dyson sphere around a black hole. They analyzed black holes of three different sizes: those five, 20 and 4 million times the mass of our Sun. These, respectively, reflect the lower and upper limits of black holes known to have formed from the collapse of massive stars—and the even more enormous mass of Sagittarius A*, the supermassive massive black hole thought to lurk at the center of the Milky Way.
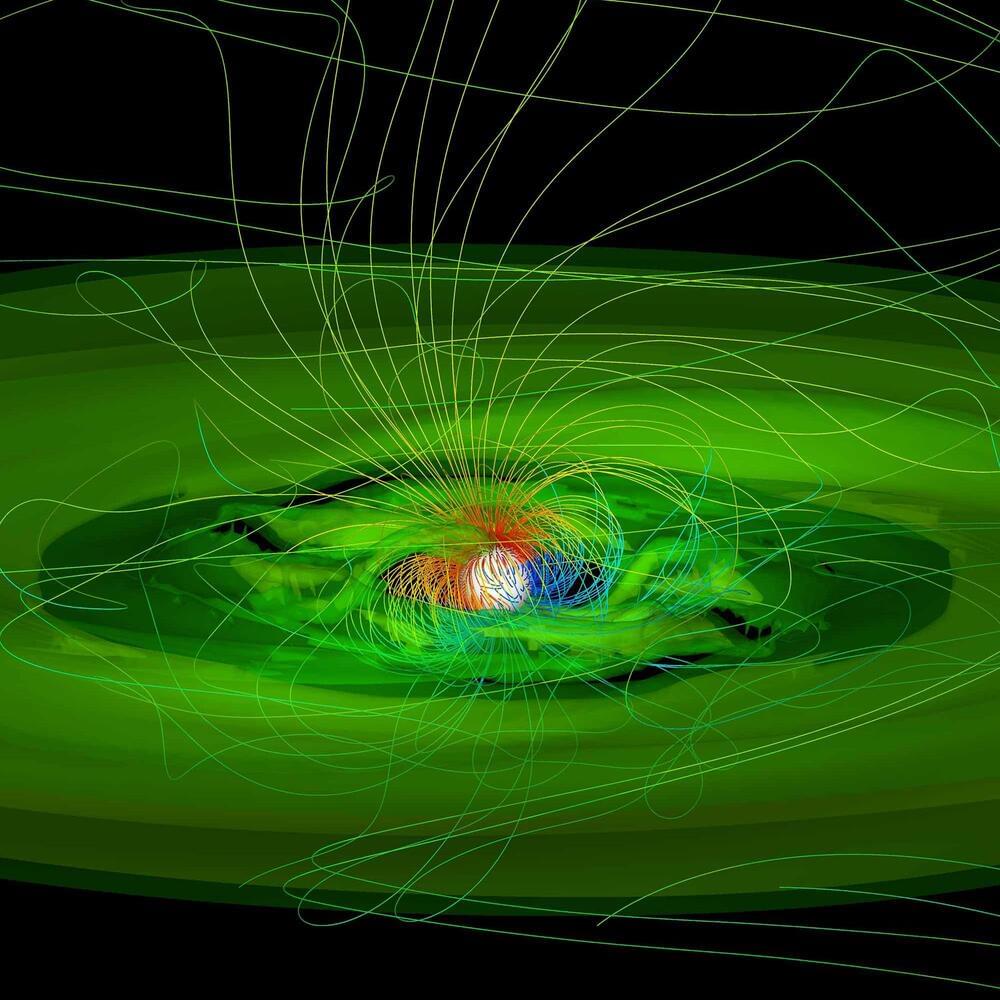
Black holes are typically thought of as consumers rather than producers of energy. Yet their huge gravitational fields can generate power through several theoretical processes. These include the radiation emitted from the accumulation of gas around the hole, the spinning “accretion” disk of matter slowly falling toward the event horizon, the relativistic jets of matter and energy that shoot out along the hole’s axis of rotation, and Hawking radiation—a theoretical way that black holes can lose mass, releasing energy in the process.
From their calculations, Hsiao and colleagues concluded that the accretion disk, surrounding gas, and jets of black holes can all serve as viable energy sources. In fact, the energy from the accretion disk alone of a stellar black hole of 20 solar masses could provide the same amount of power as Dyson spheres around 100,000 stars, the team will report next month in the. Were a supermassive black hole harnessed, the energy it could provide might be 1 million times larger still.