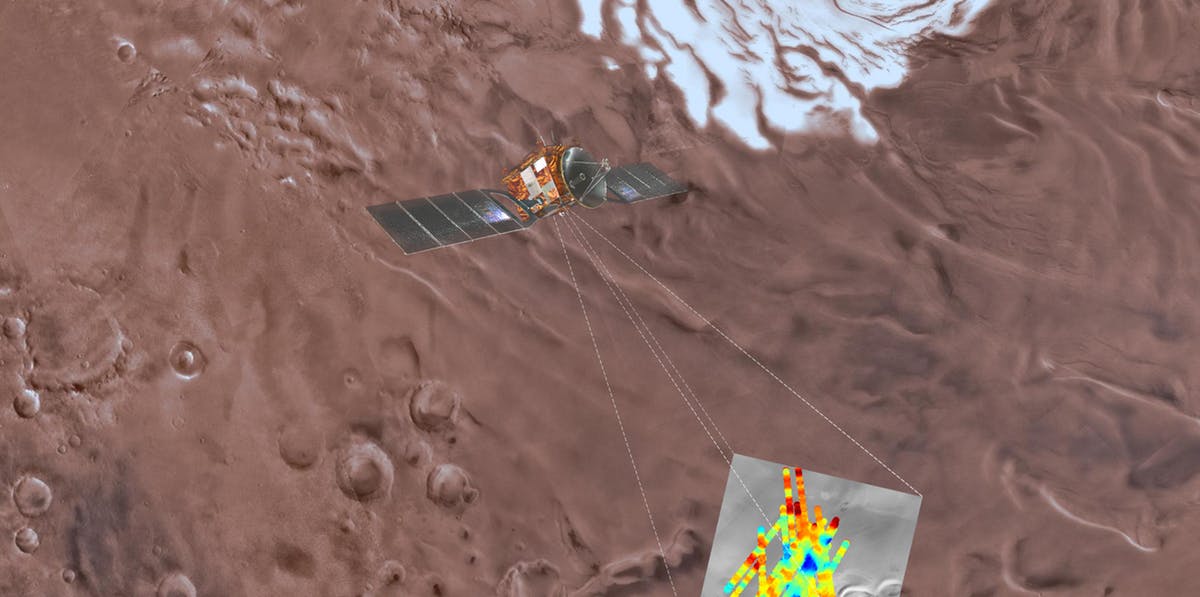
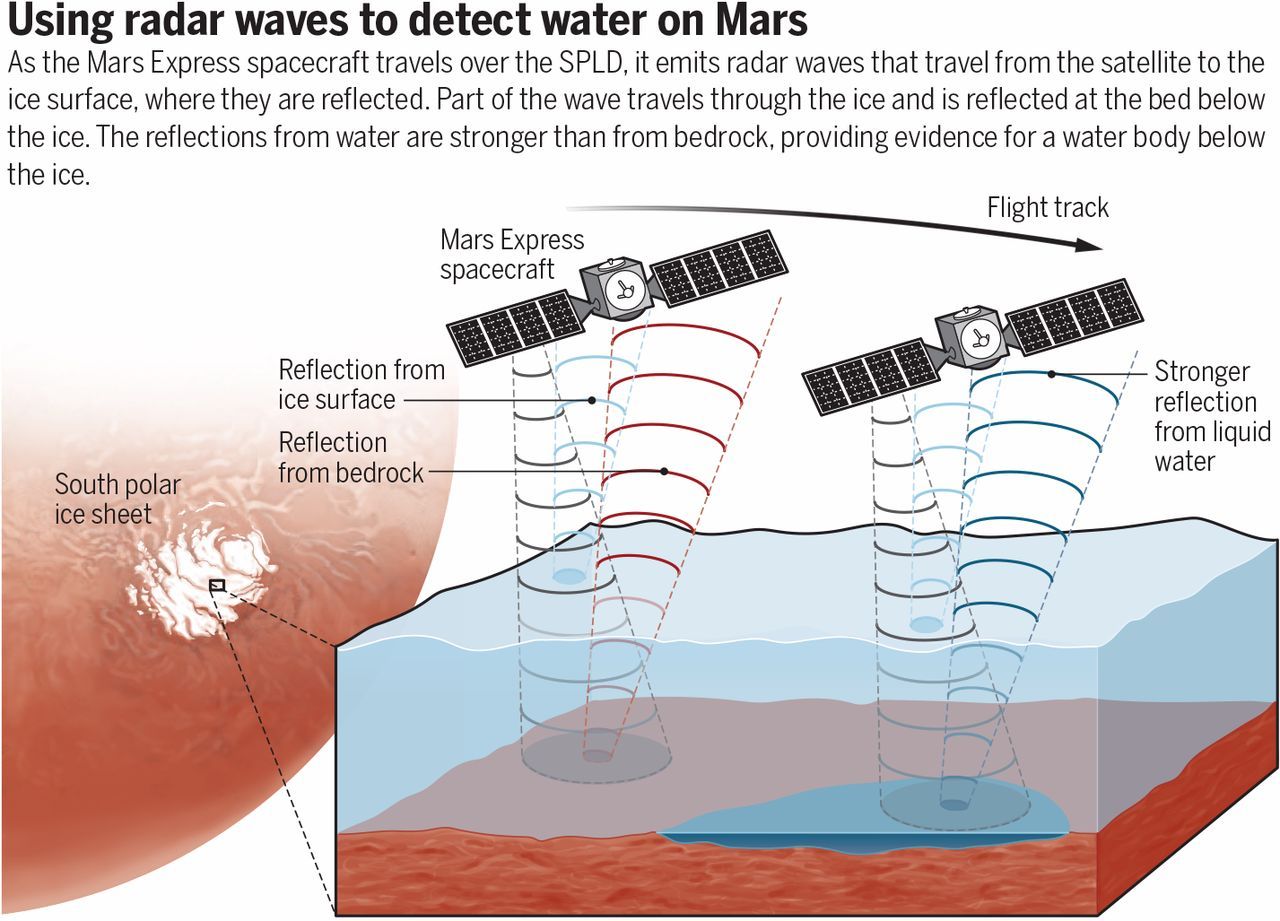
A water body exists below the Martian south polar ice cap.
Without water, no form of life as we know it could exist. There is therefore great interest in detecting liquid water on other planets of our Solar System. Landforms such as dry river valleys and lakes show that liquid water must have been present on Mars in the past (1). Nowadays, small amounts of gaseous water exist in the Martian atmosphere, and some water ice is found on the planet’s surface. Water droplets were seen condensing onto the Phoenix lander (2), and there may be reoccurring water activity on slopes during the Martian summer (3). However, stable bodies of liquid water have not been found on Mars. Published in Science’s First Release this week, Orosei et al. (4) report an analysis of radar data from the Mars Express mission that shows the existence of stable liquid water below 1.5 km of ice, close to the Martian south pole.
Ice caps similar to those on Earth exist at the Martian north and south poles, known as the North and South Polar Layered Deposits (NPLD and SPLD, respectively). More than 30 years ago, Clifford hypothesized that liquid water might be present below the Martian polar ice caps (5). Despite mean annual air temperatures of around −60°C, lakes exist below Earth’s Antarctic ice sheet (6). Glacier ice insulates the bed from the cold surface. Thus, temperatures at the base of the Antarctic ice sheet, which may be as thick as 4.8 km, can reach the pressure melting point of water; the melting point is reduced owing to the pressure of the ice layer above. Water at the ice base reduces basal friction, leading to increased flow speeds. Finding liquid water below the Martian ice caps might solve ongoing debates about whether the NPLD ice flow is due to ice deformation, deformation of the bed, or gliding over the bed or whether it is not flowing at all (7).