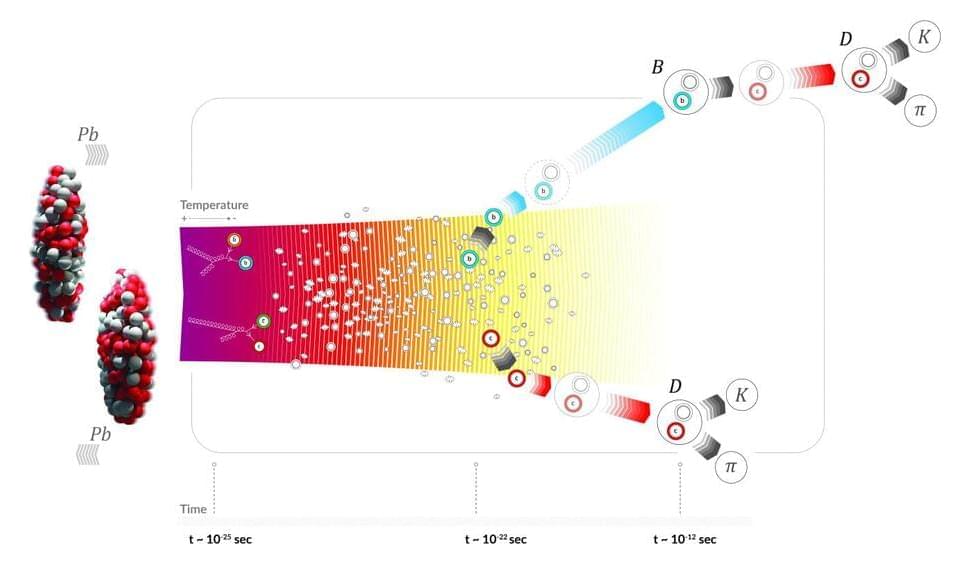
When two lead ions collide at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC), they produce an extremely hot and dense state of matter in which quarks and gluons are not confined inside composite particles called hadrons. This fireball of particles—known as quark–gluon plasma and believed to have filled the universe in the first few millionths of a second after the Big Bang—expands and cools down rapidly. The quarks and gluons then transform back into hadrons, which fly out of the collision zone towards particle detectors.
In collisions where the two lead ions do not collide head on, the overlap region between the ions has an elliptic shape that leaves an imprint on the flow of hadrons. Measurements of such elliptic flow provide a powerful way to study quark–gluon plasma. In a recent paper posted to the arXiv preprint server, the ALICE collaboration reported a new measurement of the elliptic flow of hadrons containing heavy quarks, which are particularly powerful probes of the plasma.
Unlike the gluons and light quarks that make up the bulk of the quark–gluon plasma created in heavy-ion collisions, heavy charm and beauty quarks are produced in the initial stages of the collisions, before the plasma forms. They therefore interact with the plasma throughout its entire evolution, from its expansion and cooling to its transformation into hadrons.









Comments are closed.