Proteins are involved in every biological process, and use the energy in the body to alter their structure via mechanical movements. They are considered biological ‘nanomachines’ because the smallest structural change in a protein has a significant effect on biological processes. The development of nanomachines that mimic proteins has received much attention to implement movement in the cellular environment. However, there are various mechanisms by which cells attempt to protect themselves from the action of these nanomachines. This limits the realization of any relevant mechanical movement of nanomachines that could be applied for medical purposes.
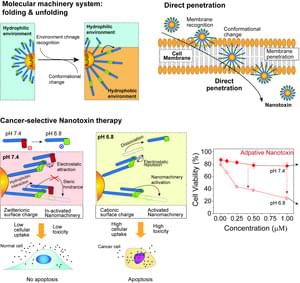
The research team led by Dr. Youngdo Jeong from the Center for Advanced Biomolecular Recognition at the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST, President Seok-Jin Yoon) has reported the development of a novel biochemical nanomachine that penetrates the cell membrane and kills the cell via the molecular movements of folding and unfolding in specific cellular environments, such as cancer cells, as a result of a collaboration with the teams of Prof. Sang Kyu Kwak from the School of Energy and Chemical Engineering and Prof. Ja-Hyoung Ryu from the Department of Chemistry at the Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST, President Yong Hoon Lee), and Dr. Chaekyu Kim of Fusion Biotechnology, Inc.
The joint research team focused on the hierarchical structure of proteins, in which the axis of the large structure and the mobile units are hierarchically separated. Therefore, only specific parts can move around the axis. Most existing nanomachines have been designed so that the mobile components and axis of the large structure are present on the same layer. Thus, these components undergo simultaneous movement, which complicates the desired control of a specific part.








Comments are closed.