Periodic prolonged fasting (PF) extends lifespan in model organisms and ameliorates multiple disease states both clinically and experimentally owing, in part, to its ability to modulate the immune system. However, the relationship between metabolic factors, immunity, and longevity during PF remains poorly characterized especially in humans.
This study aimed to observe the effects of PF in human subjects on the clinical and experimental markers of metabolic and immune health and uncover underlying plasma-borne factors that may be responsible for these effects.
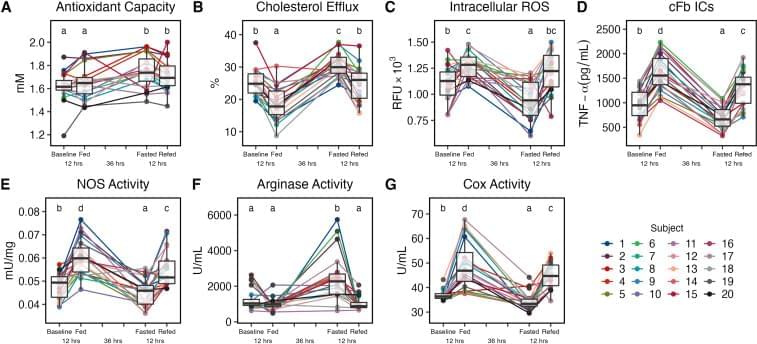
In this rigorously controlled pilot study ( ClinicalTrial.gov identifier, NCT03487679), 20 young males and females participated in a 3D study protocol including assessments of 4 distinct metabolic states: 1) overnight fasted baseline state, 2) 2-h postprandial fed state, 3) 36-h fasted state, and 4 ) final 2-h postprandial re-fed state 12 h after the 36-h fasting period. Clinical and experimental markers of immune and metabolic health were assessed for each state along with comprehensive metabolomic profiling of participant plasma. Bioactive metabolites identified to be upregulated in circulation after 36 h of fasting were then assessed for their ability to mimic the effects of fasting in isolated human macrophage as well as the ability to extend lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegans.








Comments are closed.