At team of researchers at Stanford University reports evidence that people who engage in cyclic sighing breathing exercises see a greater reduction in stress than those engaging in mindfulness meditation. In their paper published in the journal Cell Reports Medicine, the researchers describe their study of several different types of stress reduction techniques.
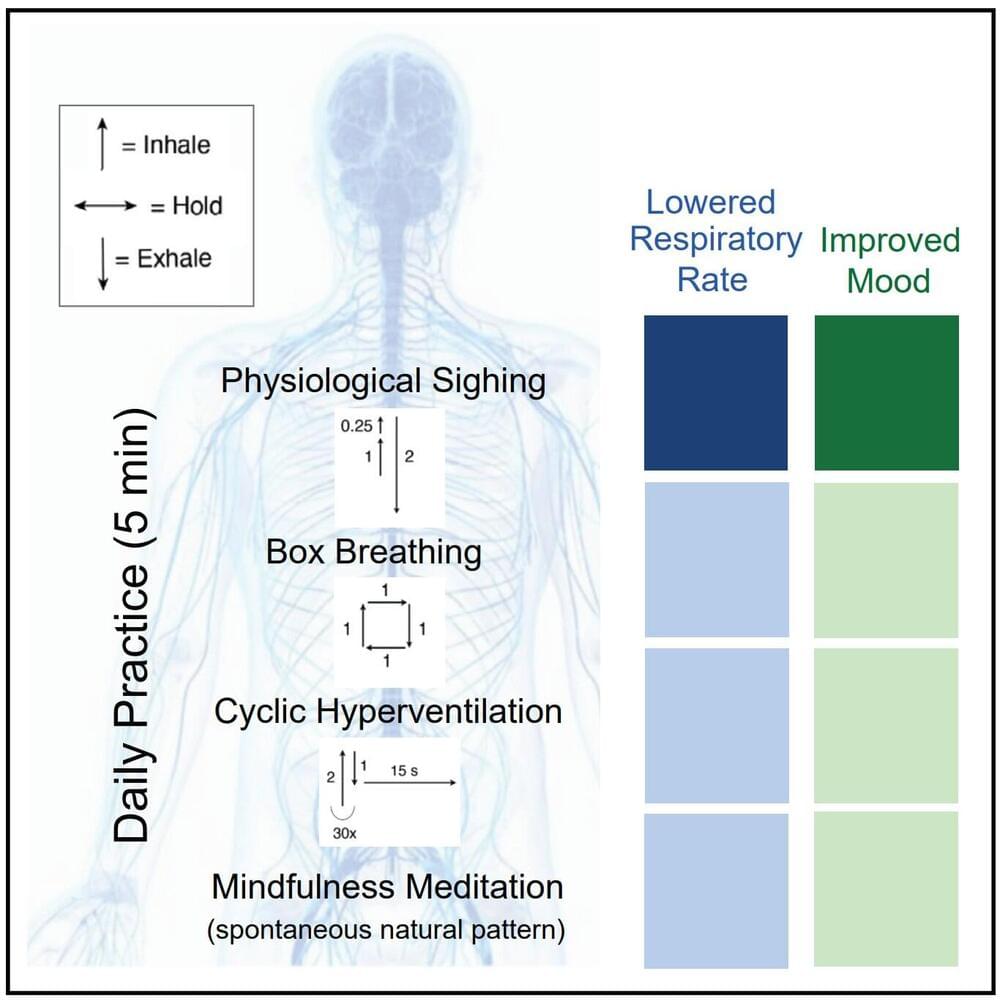
Prior research has shown that while stress can be a positive influence at times, such as when it prompts people to do things they know they need to do, more often, it is considered adverse because it can lead to health problems such as hypertension. Thus, stress techniques have been developed to help people reduce stress without resorting to drugs. One such technique is mindfulness meditation, during which a person attempts to relax by putting themselves in the moment in a nonjudgmental way for a period of time. Other techniques involve engaging in breathing exercises. In this new effort, the researchers compared three types of breathing exercises and mindfulness meditation to assess their effectiveness.
The three types of breathing exercises tested included cyclic sighing, in which more time and thought is spent on exhaling than on inhaling or holding the breath; box breathing, in which breathing and holding are done for the same amount of time; and cyclic hyperventilation, in which inhalations last longer than exhalations.









Comments are closed.