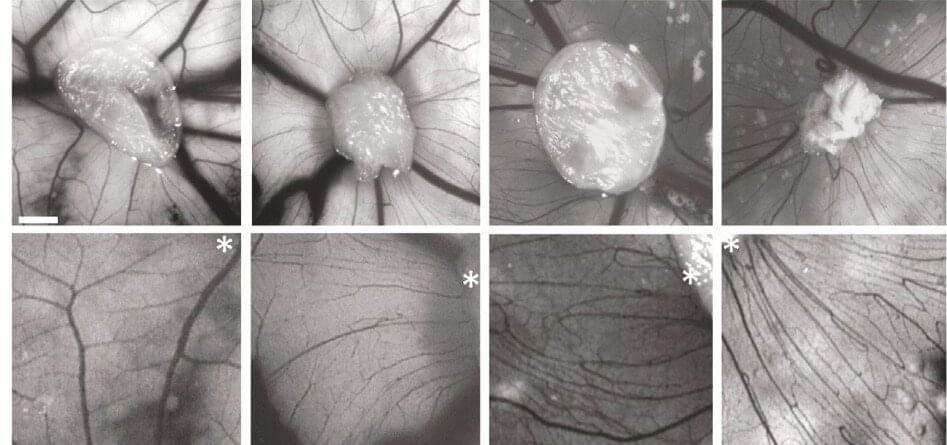
A study conducted in Brazil and reported in an article published in Molecular Psychiatry suggests that schizophrenia may be associated with alterations in the vascularization of certain brain regions. Researchers at the State University of Campinas (UNICAMP), D’Or Research and Education Institute (IDOR) and the Federal University of Rio de Janeiro (UFRJ) found a link between astrocytes (central nervous system cells) from patients with schizophrenia and formation of narrow blood vessels.
Schizophrenia is a severe multifactorial mental health disorder affecting around 1% of the world population. Common symptoms include loss of contact with reality (psychosis), hallucinations (hearing voices, for example), delusions or delirium, disorganized motor behavior, loss of motivation and cognitive impairment.
In the study, the researchers focused on the role of astrocytes in development of the disease. These glial cells are housekeepers of the central nervous system and important to its defense. They are the central elements of the neurovascular units that integrate neural circuitry with local blood flow and provide neurons with metabolic support.