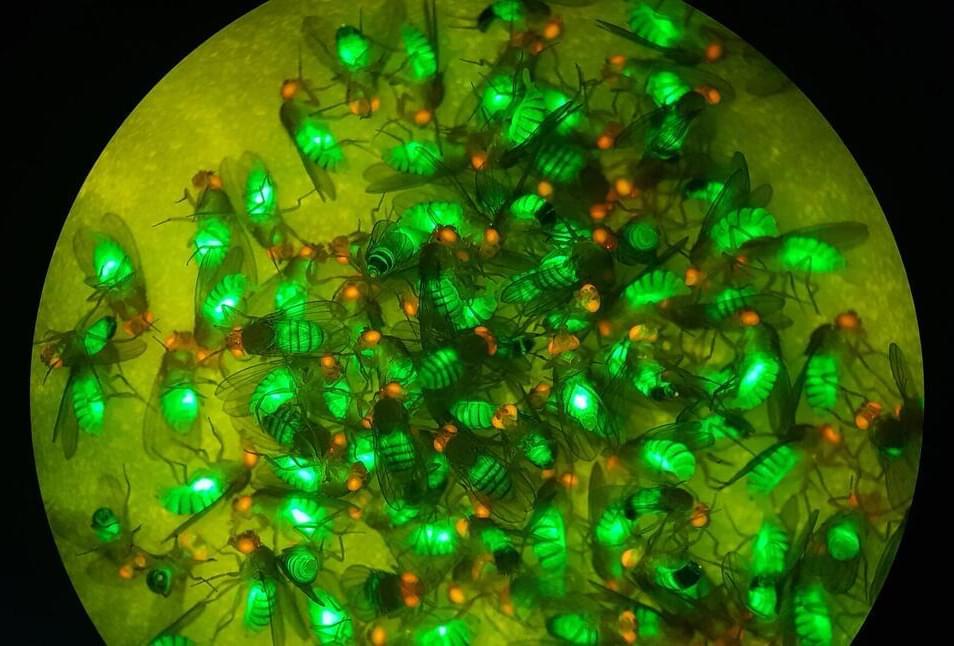
Scientists continue to expand the technological frontiers of CRISPR, along with its enormous potential, in areas ranging from human health to global food supplies. Such is the case with CRISPR-based gene drives, a genetic editing tool designed to influence how genetic elements are passed from one generation to the next.
Gene drives designed for mosquitoes have the potential to curb the spread of malarial infections that cause hundreds of thousands of deaths each year, yet safety issues have been raised because such drives can spread quickly and dominate entire populations. Scientists have explored the principles governing the spread of gene-drive elements in targeted populations such as mosquitoes by testing many different combinations of components that constitute the drive apparatus. They have found, however, that there’s still more to explore and that key questions remain.
In the journal Nature Communications, University of California San Diego researchers led by former Postdoctoral Scholar Gerard Terradas, together with Postdoctoral Scholar Zhiqian Li and Professor Ethan Bier, in close collaboration with UC Berkeley graduate student Jared Bennett and Associate Professor John Marshall, describe the development of a new system for testing and developing gene drives in the laboratory and safely converting them into tools for potential real-world applications.