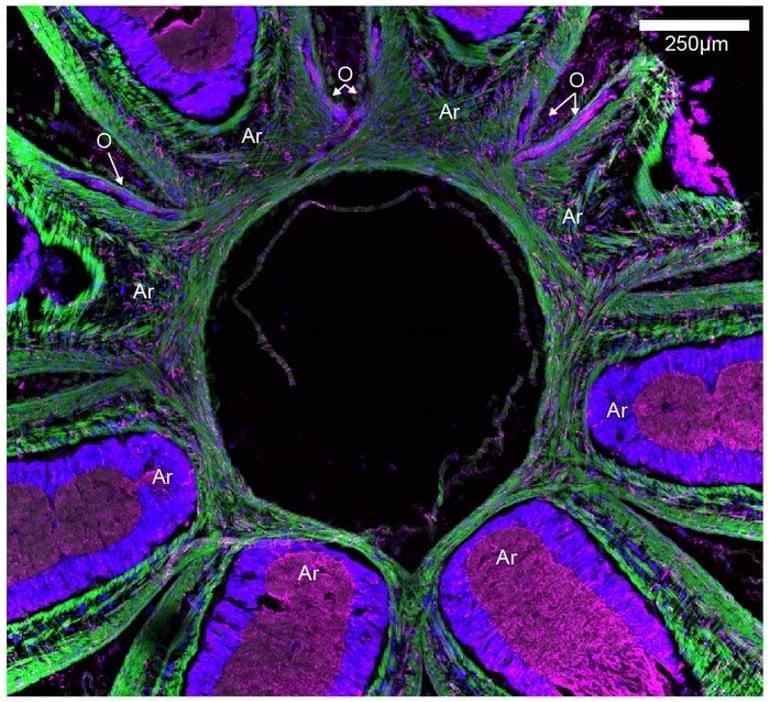
Summary: Researchers discovered a structure within the octopus nervous system by which the intramuscular nerve cords, which help the cephalopod to sense its arm movements, connect arms on the opposite side of the animal.
Source: University of Chicago.
Octopuses are not much like humans — they are invertebrates with eight arms, and more closely related to clams and snails. Still, they have evolved complex nervous systems with as many neurons as in the brains of dogs, and are capable of a wide array of complicated behaviors.









Comments are closed.