Electrolysis is a key component of the cost of green hydrogen, and a Korean team says it’s made a huge breakthrough with an anion exchange membrane that’s not only much cheaper than current proton exchange tech, but offers some 20 percent better performance.
Electrolysis is the process of splitting water into hydrogen and oxygen, and when powered by renewable energy, it’s shaping up to be a key step in the production of green hydrogen. Green hydrogen is set to play a substantial role in the race to zero emissions, offering a high energy density that makes it an attractive option in several hard-to-decarbonize activities where batteries just don’t make sense.
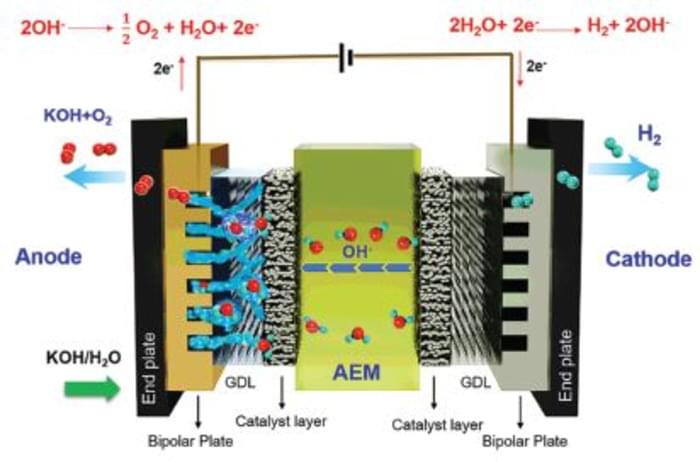
Typically, electrolyzers use proton exchange membranes (PEMs), in which an anode and a cathode in an electrolyte material are separated by a membrane designed to allow positively-charged hydrogen ions to pass through as they’re attracted by the cathode. Here they combine with electrons to form hydrogen gas, which is collected, and oxygen is released at the anode.