Despite the traditional view that species do not exchange genes by hybridisation, recent studies show that gene flow between closely related species is more common than previously thought. A team of scientists from Uppsala University and Princeton University now reports how gene flow between two species of Darwin’s finches has affected their beak morphology. The study is published today in Nature Ecology and Evolution.
Darwin’s finches on the Galápagos Islands are an example of a rapid adaptive radiation in which 18 species have evolved from a common ancestral species within a period of 1–2 million years. Some of these species have only been separated for a few hundred thousand years or less.
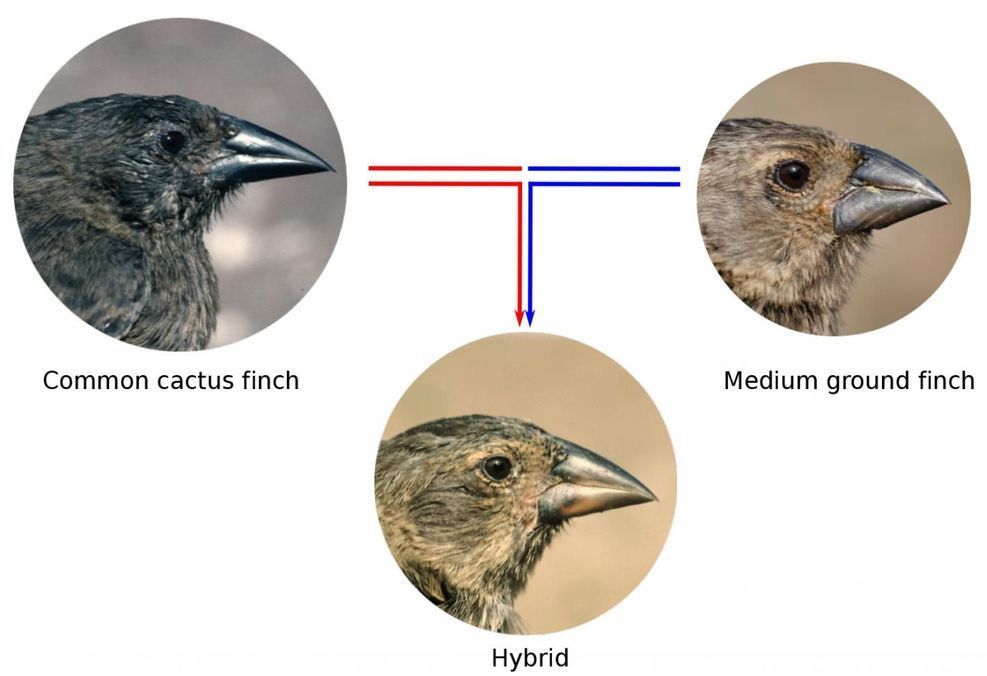
Rosemary and Peter Grant of Princeton University, co-authors of the new study, studied populations of Darwin’s finches on the small island of Daphne Major for 40 consecutive years and observed occasional hybridisation between two distinct species, the common cactus finch and the medium ground finch. The cactus finch is slightly larger than the medium ground finch, has a more pointed beak and is specialised to feed on cactus. The medium ground finch has a blunter beak and is specialised to feed on seeds.








Comments are closed.