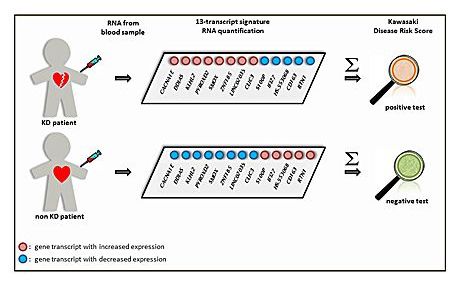
For the first time, researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine and Imperial College London, with international collaborators, have determined that Kawasaki disease (KD) can be accurately diagnosed on the basis of the pattern of host gene expression in whole blood. The finding could lead to a diagnostic blood test to distinguish KD from other infectious and inflammatory conditions.
Results of the international study published on August 6 in JAMA Pediatrics.
Kawasaki disease is the most common acquired heart disease in children. Untreated, roughly one-quarter of children with KD develop coronary artery aneurysms — balloon-like bulges of heart vessels — that may ultimately result in heart attacks, congestive heart failure or sudden death.









Comments are closed.