Nice.
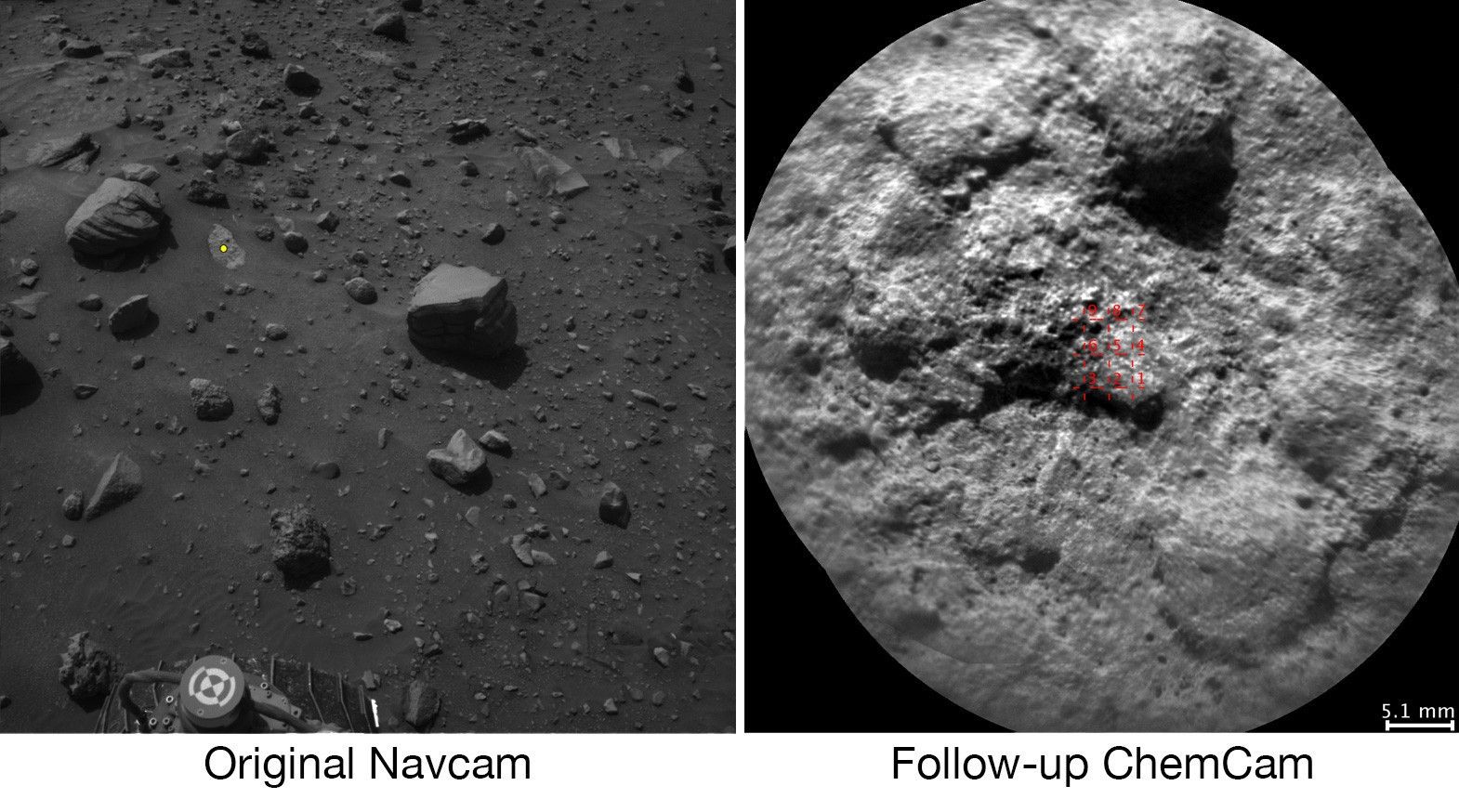
Who’s calling the shots now? After nearly four years on the job, NASA’s Curiosity rover is finally making certain scientific decisions on its own. The Martian explorer now picks some of the rock targets to blast with the laser on its ChemCam instrument.
A software upgrade known as AEGIS allows the rover to make key decisions when Mars is out of sync with Curiosity’s handlers at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, delivering more data in less time. It’s the first time a robot has been able to choose such science targets autonomously on any planetary mission.
“Time on Mars is valuable and we get more data this way and we get the data much faster,” said AEGIS team member Raymond Francis, a scientific applications software engineer at JPL.








Comments are closed.