Mar 29, 2018
China sends twin BeiDou-3 navigation satellites into space
Posted by Genevieve Klien in category: satellites
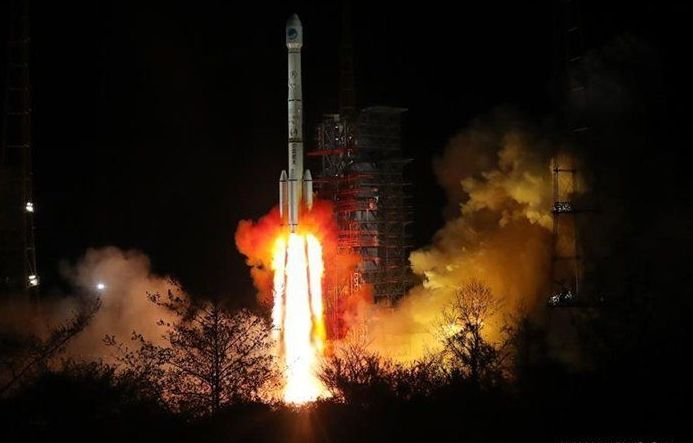
China on Friday sent twin satellites into space with a single carrier rocket, adding two more members for its domestic BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS).
The Long March-3B carrier rocket lifted off from Xichang Satellite Launch Center in southwest China’s Sichuan Province at 1:56 a.m. The launch was the 269th mission for the Long March rocket family.
The twin satellites are coded as the 30th and 31st satellites in the BDS.