Page 9138
Feb 6, 2019
Breakthrough device llures aggressive brain tumor cells out of the patient
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: biotech/medical, neuroscience
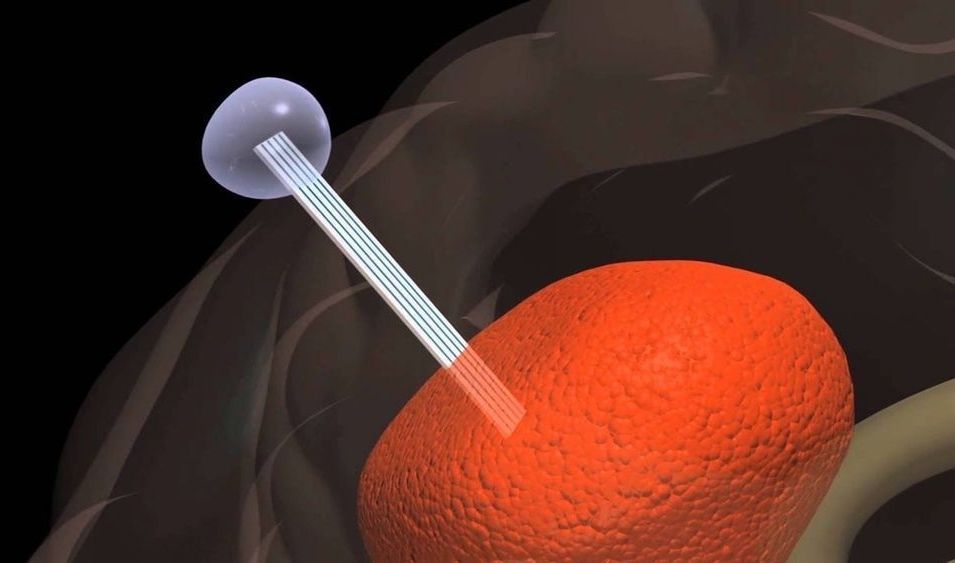
A biomedical tool that tricks aggressive brain tumors such as glioblastoma into migrating into an external container rather than throughout the brain has been designated a “Breakthrough Device” by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Dubbed the Tumor Monorail, the device mimics the physical properties of the brain’s white matter to entice aggressive tumors to migrate toward the exterior of the brain, where the migrating cells can be collected and removed. The purpose of the device is not to destroy the tumor, but to halt its lethal spread, making the disease more of a condition to manage than a death sentence.
Continue reading “Breakthrough device llures aggressive brain tumor cells out of the patient” »
Feb 6, 2019
DHL adding 63 electric vans to US fleet
Posted by Quinn Sena in category: transportation

https://youtube.com/watch?v=uTRIcoR4qRM
Slowly but surely, home delivery is getting cleaner.
Logistics company DHL has already branched out into selling its own StreetScooter zero emission delivery vehicles, but that doesn’t mean it’s not in the market for adding to its fleet from other manufacturers either.
Continue reading “DHL adding 63 electric vans to US fleet” »
Feb 6, 2019
A New “Solar Paint” Lets You Transform Your Entire House Into a Source of Clean Energy
Posted by Quinn Sena in category: energy
Feb 6, 2019
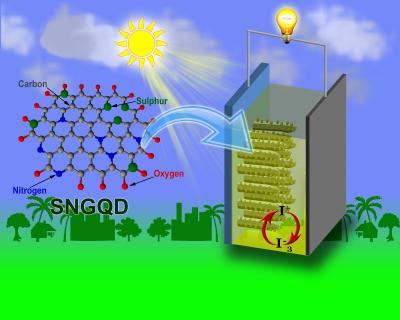
Graphene quantum dots sensitized C-ZnO nanotaper photoanodes for solar cells application
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: quantum physics, solar power, sustainability
In a paper to be published in the forthcoming issue in NANO, researchers from the National Institute of Technology, India, have synthesized blue-green-orange photoemissive sulfur and nitrogen co-doped graphene quantum dots (SNGQDs) using hydrothermal method. These GQDs showed strong UV-visible photoabsorption and excitation dependent photoemission which have low-cost, eco-friendly solar cell application.
Feb 6, 2019
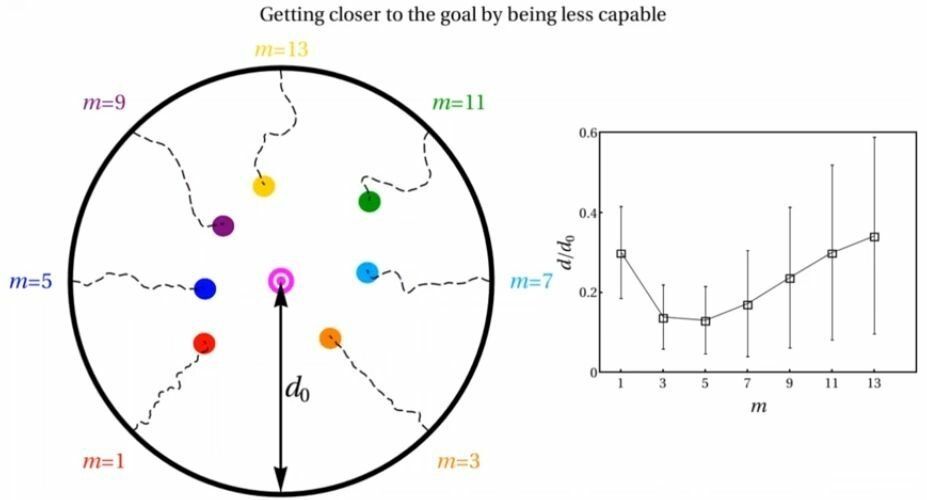
Decentralized systems are more efficient at reaching a target when its components are not overly capable
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: information science, robotics/AI, transportation
A team of researchers including Neil Johnson, a professor of physics at the George Washington University, has discovered that decentralized systems work better when the individual parts are less capable.
Dr. Johnson was interested in understanding how systems with many moving parts can reach a desired target or goal without centralized control. This explores a common theory that decentralized systems, those without a central brain, would be more resilient against damage or errors.
This research has the potential to inform everything from how to effectively structure a company, build a better autonomous vehicle, optimize next-generation artificial intelligence algorithms—and could even transform our understanding of evolution. The key lies in understanding how the “sweet spot” between decentralized and centralized systems varies with how clever the pieces are, Dr. Johnson said.
Feb 6, 2019
Move Over, Spintronics: Here Comes Magnonics to the Rescue of Electronics
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: electronics, particle physics
New type of logic gate promises to completely replace electricity with magnetic spin waves for computation.
Feb 6, 2019
Ancient Druid Healing ‘Treatment’ Shows Potential For Killing Today’s Superbugs
Posted by Quinn Sena in category: biotech/medical
Faced with the rising threat of drug resistant pathogens, researchers are all but giving up hope that new treatments can be easily cooked up in the lab.
One recent discovery gives us hope that novel antibiotics are easier to find than we think, perhaps in plain sight right under our very feet. And it’s possible their curative properties could have already been recognised centuries in the past.
An international team of researchers based at Swansea University Medical School in South West Wales recently identified a new strain of bacterium in ‘healing soil’ taken from a site associated with ancient druidic rituals in Northern Ireland.
Continue reading “Ancient Druid Healing ‘Treatment’ Shows Potential For Killing Today’s Superbugs” »
Feb 6, 2019
Ebola Vaccinations Expanding in Central Africa
Posted by Quinn Sena in category: biotech/medical
The African country of South Sudan has started vaccinating front-line response staff with the Ebola Zaire vaccine candidate v920.
The vaccine’s producer, Merck, has given 2,160 doses of the vaccine candidate V920 (rVSV-ZEBOV) as part of preparedness measures to fight the spread of the Ebola disease, said the World Health Organization (WHO) in a press release on January 28, 2019.
This preventive effort is in reaction to South Sudan’s neighboring country the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), which is now experiencing its 10th Ebola outbreak.
Continue reading “Ebola Vaccinations Expanding in Central Africa” »
Feb 6, 2019
Superhuman Skin Senses Sound Waves and Magnetic Fields
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: biotech/medical, cyborgs, nanotechnology, wearables
Researchers have developed a new kind of sensor designed to let artificial skin sense pressure, vibrations, and even magnetic fields. Developed by engineers, chemists, and biologists at the University of Connecticut and University of Toronto, the technology could help burn victims and amputees “feel” again through their prosthetic skin.
“The type of artificial skin we developed can be called an electronic skin or e-skin,” Islam Mosa, a postdoctoral fellow at UConn, told Digital Trends. “It is a new group of smart wearable electronics that are flexible, stretchable, shapable, and possess unique sensing capabilities that mimic human skin.”
To create the sensor for the artificial skin, Mosa and his team wrapped a silicone tube with a copper wire and filled the tube with an iron oxide nanoparticle fluid. As the nanoparticles move around the tube, they create an electrical current, which is picked up by the copper wire. When the tube experiences pressure, the current changes.