Page 9083
Nov 20, 2018
Lasers may help experts understand cancer
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: biotech/medical, nanotechnology, neuroscience
Scientists in Fife are investigating if tiny lasers could be used to better understand diseases such as cancer.
Using nano-technology, the St Andrews University experts created lasers small enough to fit inside live cells which can then be tracked.
With a diameter of a thousandth of a millimetre, the lasers can be inserted into neurons or immune cells.
Nov 20, 2018
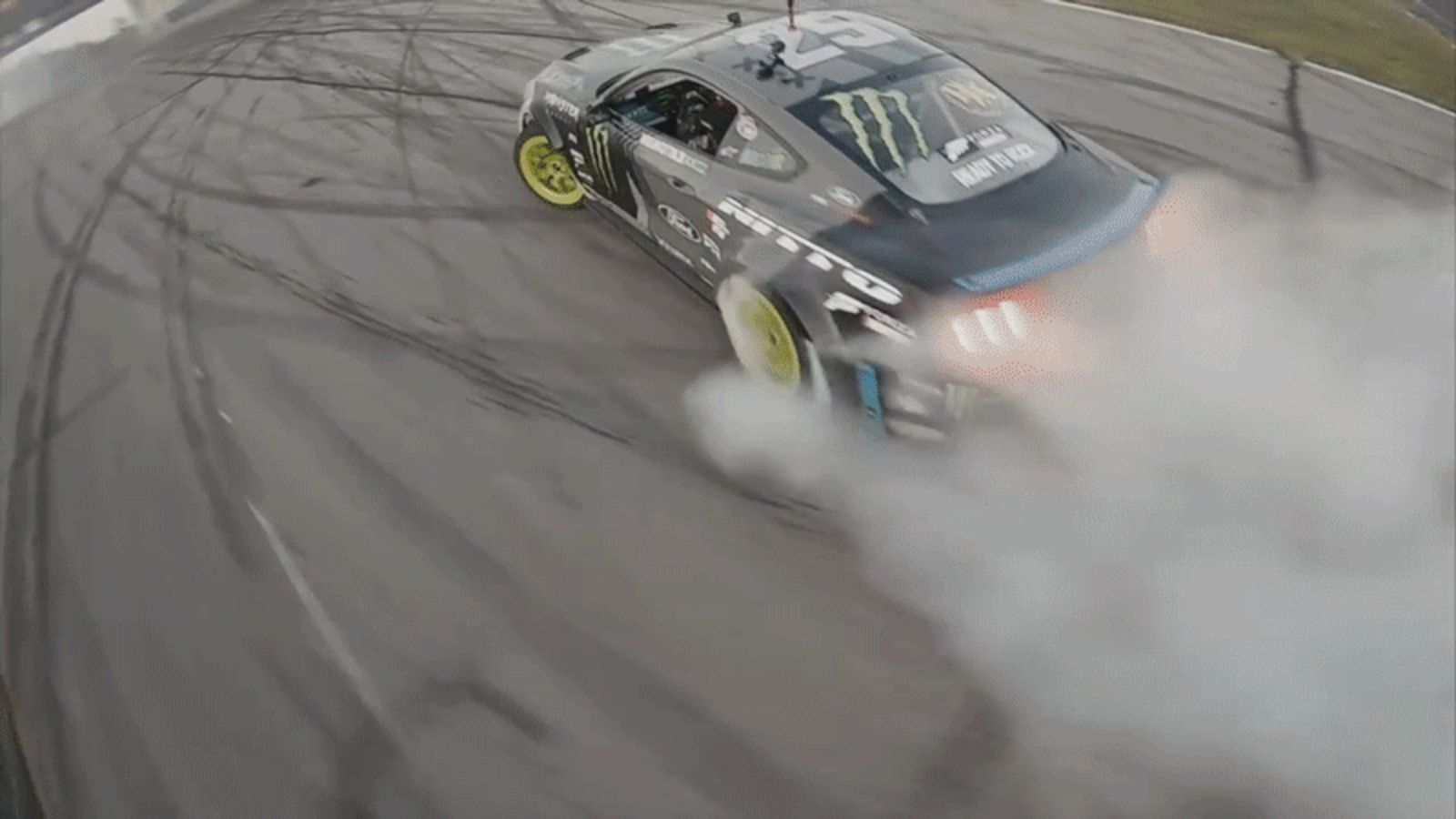
This Guy Has to Be One of the Best Drone Pilots in The World
Posted by Genevieve Klien in category: drones
A few years ago I wrote about how YouTube opened up rallying to the world in a way that it never had before, taking the sport out of forests and onto screens everywhere. I didn’t expect the same of drones and drifting but here we are.
Nov 20, 2018
When AI and optoelectronics meet: Researchers take control of light properties
Posted by Genevieve Klien in category: robotics/AI
Using machine-learning and an integrated photonic chip, researchers from INRS (Canada) and the University of Sussex (UK) can now customize the properties of broadband light sources. Also called “supercontinuum”, these sources are at the core of new imaging technologies and the approach proposed by the researchers will bring further insight into fundamental aspects of light-matter interactions and ultrafast nonlinear optics. The work is published in the journal Nature Communications on November 20, 2018.
Nov 20, 2018
We’re going to Jezero!
Posted by Alberto Lao in categories: chemistry, climatology, space
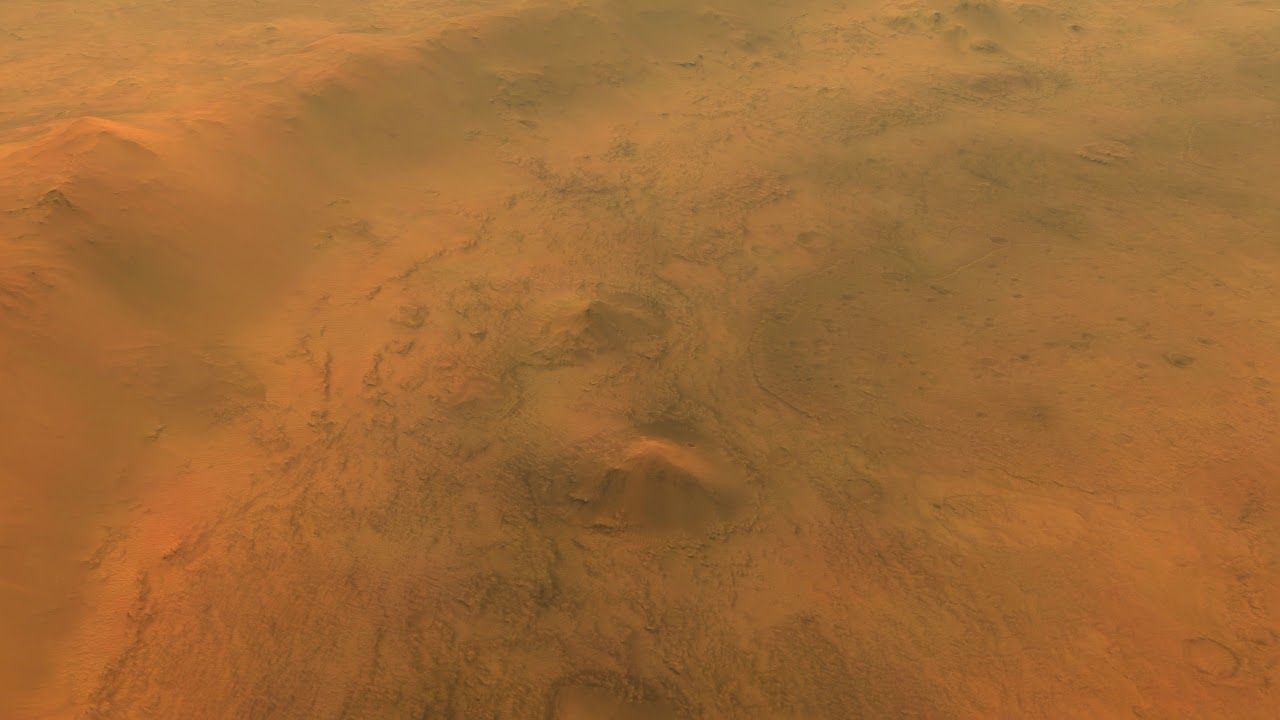
At Jezero, Mars 2020’s goal will be “to explore the history of water and chemistry in an ancient crater lake basin and associated river-delta environments to probe early Martian climates and search for life.”
NASA announced this morning the selection of Jezero crater for the landing site of the Mars 2020 mission. Jezero is a 45-kilometer-wide crater that once held a lake, and now holds a spectacular ancient river delta.
Nov 20, 2018
Deep sea mining zone hosts carbon dioxide-consuming bacteria, scientists discover
Posted by Genevieve Klien in category: food
Scientists have discovered that bacteria in the deepest parts of the seafloor are absorbing carbon dioxide and could be turning themselves into an additional food source for other deep-sea life.
Nov 20, 2018
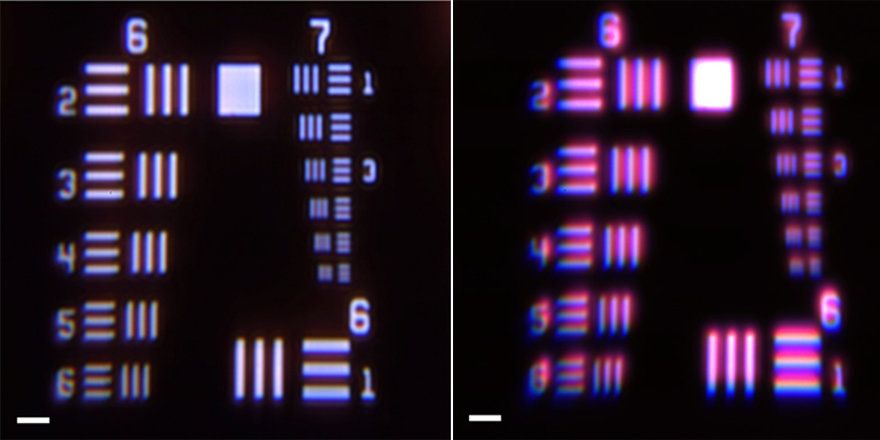
Meta-surface corrects for chromatic aberrations across all kinds of lenses
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: materials, mobile phones
Today’s optical systems—from smartphone cameras to cutting-edge microscopes—use technology that hasn’t changed much since the mid-1700s. Compound lenses, invented around 1730, correct the chromatic aberrations that cause lenses to focus different wavelengths of light in different spots. While effective, these multi-material lenses are bulky, expensive, and require precision polishing or molding and very careful optical alignment. Now, a group of researchers at the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) is asking: Isn’t it time for an upgrade?
Nov 20, 2018
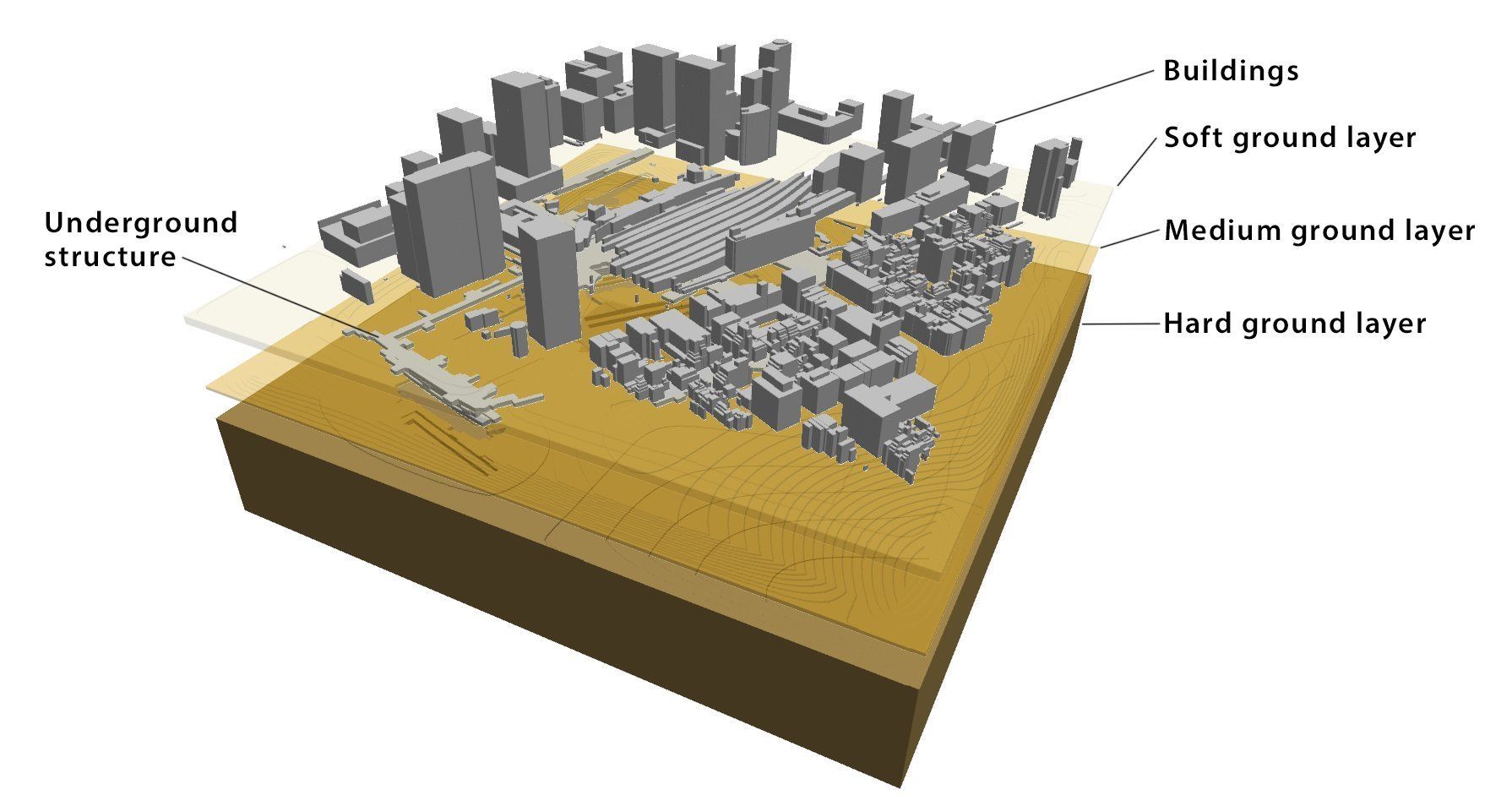
Computer scientists use artificial intelligence to boost an earthquake physics simulator
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: engineering, physics, robotics/AI
A team of researchers from the Earthquake Research Institute, Department of Civil Engineering and Information Technology Center at the University of Tokyo, and the RIKEN Center for Computational Science and RIKEN Center for Advanced Intelligence Project in Japan were finalists for the coveted Gordon Bell Prize for outstanding achievements in high-performance computing. Tsuyoshi Ichimura together with Kohei Fujita, Takuma Yamaguchi, Kengo Nakajima, Muneo Hori and Lalith Maddegedara were praised for their simulation of earthquake physics in complex urban environments.
Nov 20, 2018
On November 26th, a mole will land on Mars
Posted by Alberto Lao in category: space travel
Nov 20, 2018
Universal Quantum Phenomenon Found in Superconductors
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: materials, quantum physics
Experiments suggest that exotic superconducting materials share a “strange metal” state characterized by a quantum speed limit that somehow acts as a fundamental organizing principle.