Page 8883
Apr 30, 2019
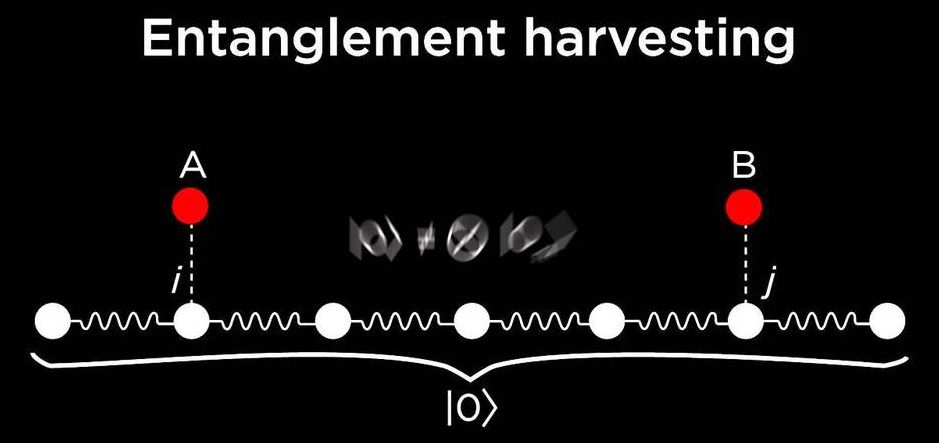
Quantum Entanglement harvesting in a vacuum
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: particle physics, quantum physics, space
Circa 2016
Entanglement is an extremely strong correlation that can exist between quantum systems. These correlations are so strong that two or more entangled particles have to be described with reference to each other, even though the individual objects may be spatially separated.
Continue reading “Quantum Entanglement harvesting in a vacuum” »
Apr 30, 2019
Diamond Nuclear Batteries Are Forever… Sort Of
Posted by Quinn Sena in category: futurism
Apr 30, 2019
Almost half of World Heritage sites could lose their glaciers by 2100
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: business, computing
Glaciers are set to disappear completely from almost half of World Heritage sites if business-as-usual emissions continue, according to the first-ever global study of World Heritage glaciers.
The sites are home to some of the world’s most iconic glaciers, such as the Grosser Aletschgletscher in the Swiss Alps, Khumbu Glacier in the Himalayas and Greenland’s Jakobshavn Isbrae.
The study in the AGU journal Earth’s Future and co-authored by scientists from the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) combines data from a global glacier inventory, a review of existing literature and sophisticated computer modeling to analyze the current state of World Heritage glaciers, their recent evolution, and their projected mass change over the 21st century.
Continue reading “Almost half of World Heritage sites could lose their glaciers by 2100” »
Apr 30, 2019
New approach predicts glass’ always-evolving behaviors at different temperatures
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: information science, particle physics
Not everything about glass is clear. How its atoms are arranged and behave, in particular, is startlingly opaque.
The problem is that glass is an amorphous solid, a class of materials that lies in the mysterious realm between solid and liquid. Glassy materials also include polymers, or commonly used plastics. While it might appear to be stable and static, glass’ atoms are constantly shuffling in a frustratingly futile search for equilibrium. This shifty behavior has made the physics of glass nearly impossible for researchers to pin down.
Now a multi-institutional team including Northwestern University, North Dakota State University and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has designed an algorithm with the goal of giving polymeric glasses a little more clarity. The algorithm makes it possible for researchers to create coarse-grained models to design materials with dynamic properties and predict their continually changing behaviors. Called the “energy renormalization algorithm,” it is the first to accurately predict glass’ mechanical behavior at different temperatures and could result in the fast discovery of new materials, designed with optimal properties.
Apr 30, 2019
“Unlimited range” stealth e-bike never needs plugging in
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: innovation, transportation
If e-bikes tend to look a little ungainly for your tastes, check out this thing from Barcelona’s Nua Bikes. With the motor, sensors and battery built into a discreet hub unit, the Nua Electrica is barely distinguishable from a regular fixie, and its innovative “self-charging” mode means you can get away without ever charging it.
Apr 30, 2019
The science behind the twisting alien linguistics of Arrival
Posted by Quinn Sena in category: science
By Rowan Hooper
Science fiction thrillers usually send in gun-toting heroes like Will Smith or Tom Cruise to kick invading alien butt. Arrival is completely, wonderfully different: it sends in a linguist, played by Amy Adams.
“Language,” one character says, “is the first weapon drawn in a conflict.” The big question to ask the aliens: what is their purpose on Earth?
Continue reading “The science behind the twisting alien linguistics of Arrival” »
Apr 30, 2019
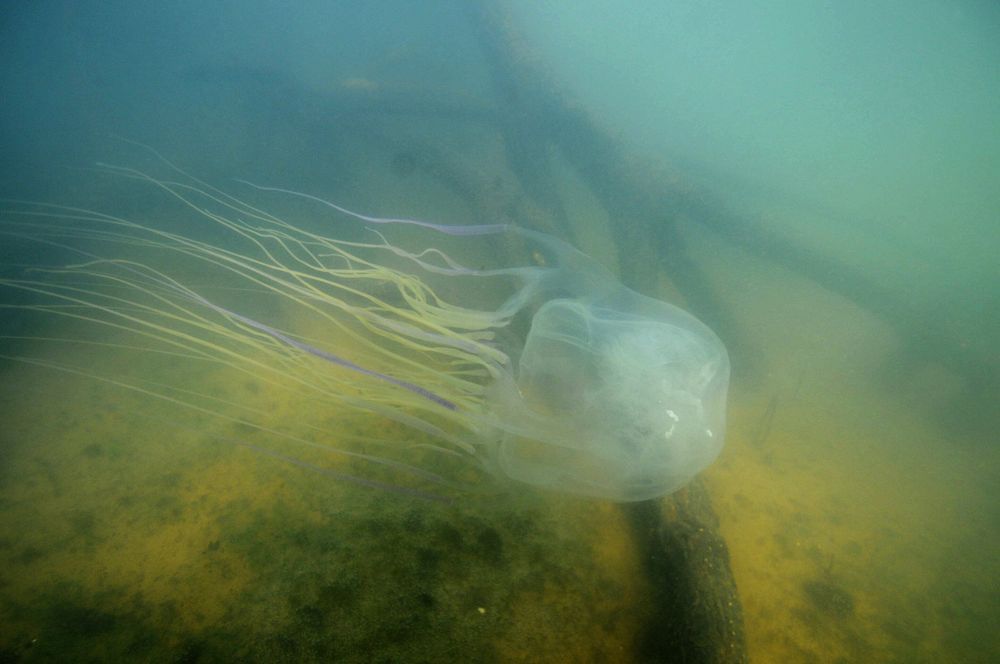
Deadly box jellyfish antidote discovered using CRISPR genome editing
Posted by Quinn Sena in category: biotech/medical
Researchers at the University of Sydney have discovered an antidote to the deadly sting delivered by the most venomous creature on earth—the Australian box jellyfish.
The Australian box jellyfish (Chironex fleckeri) has about 60 tentacles that can grow up to three metres long. Each tentacle has millions of microscopic hooks filled with venom.
Each box jellyfish carries enough venom to kill more than 60 humans.
Continue reading “Deadly box jellyfish antidote discovered using CRISPR genome editing” »
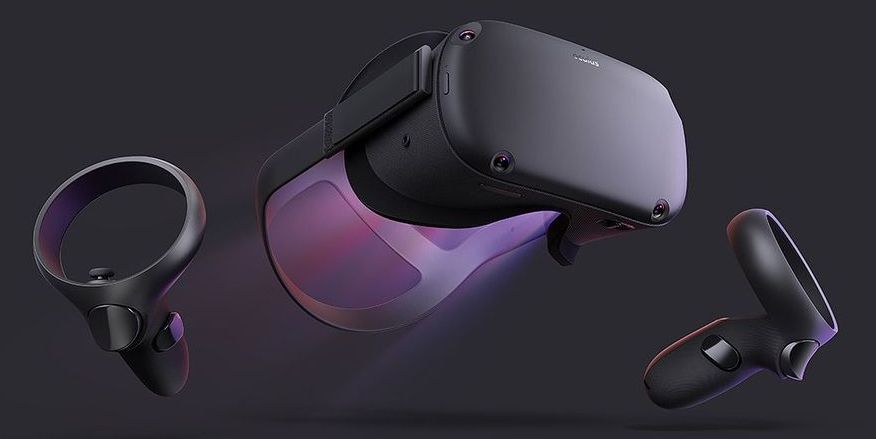
New Oculus Quest is out. VR without a PC, wireless. I have had the last two iterations of the Oculus Rift, and it is truly incredible.
Oculus Quest is our first all-in-one gaming system for virtual reality. No wires. No PC. Just a headset and controllers that transport you into another world.
Apr 30, 2019
How Twisted Graphene Became the Big Thing in Physics
Posted by Klaus Baldauf in categories: materials, physics
The stunning emergence of a new type of superconductivity with the mere twist of a carbon sheet has left physicists giddy, and its discoverer nearly overwhelmed.