May 5, 2019
Quantum sensor for photons
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: computing, internet, particle physics, quantum physics
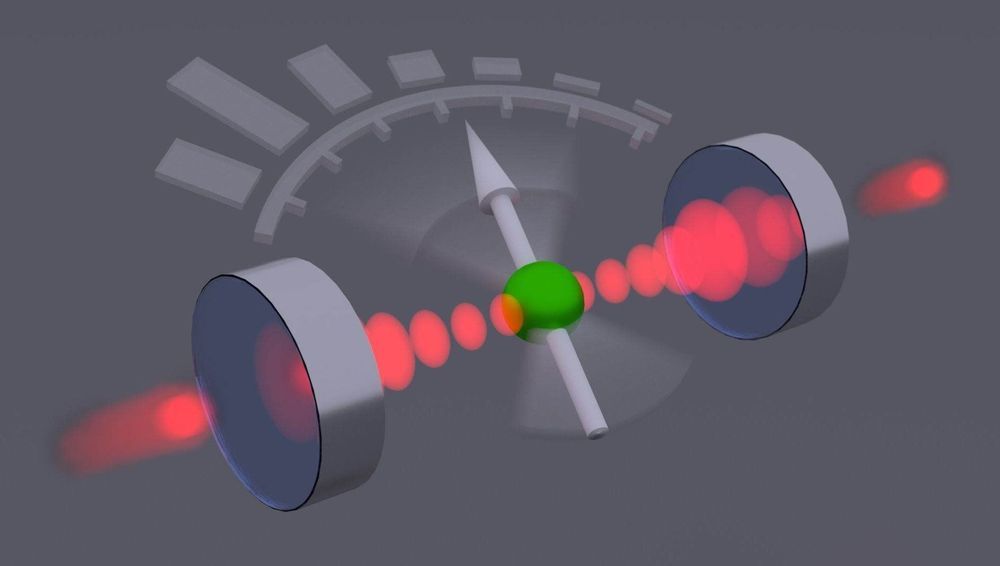
A photodetector converts light into an electrical signal, causing the light to be lost. Researchers led by Tracy Northup at the University of Innsbruck have now built a quantum sensor that can measure light particles non-destructively. It can be used to further investigate the quantum properties of light.
Physicist Tracy Northup is currently researching the development of quantum internet at the University of Innsbruck. The American citizen builds interfaces with which quantum information can be transferred from matter to light and vice versa. Over such interfaces, it is anticipated that quantum computers all over the world will be able to communicate with each other via fiber optic lines in the future. In their research, Northup and her team at the Department of Experimental Physics have now demonstrated a method with which visible light can be measured non-destructively. The development follows the work of Serge Haroche, who characterized the quantum properties of microwave fields with the help of neutral atoms in the 1990s and was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2012.
In work led by postdoc Moonjoo Lee and Ph.D. student Konstantin Friebe, the researchers place an ionized calcium atom between two hollow mirrors through which visible laser light is guided. “The ion has only a weak influence on the light,” explains Tracy Northup. “Quantum measurements of the ion allow us to make statistical predictions about the number of light particles in the chamber.” The physicists were supported in their interpretation of the measurement results by the research group led by Helmut Ritsch, a Innsbruck quantum optician from the Department of Theoretical Physics. “One can speak in this context of a quantum sensor for light particles”, sums up Northup, who has held an Ingeborg Hochmair professorship at the University of Innsbruck since 2017. One application of the new method would be to generate special tailored light fields by feeding the measurement results back into the system via a feedback loop, thus establishing the desired states.