Page 8750
Jun 2, 2019
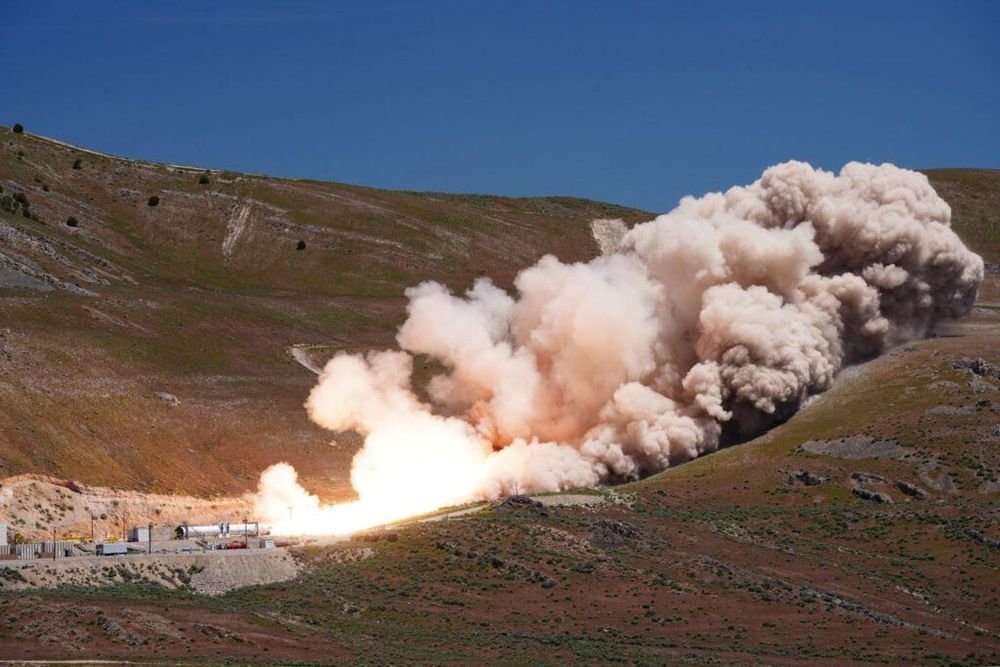
Key Northrop Grumman OmegA Rocket Test Succeeds, Despite Hiccup
Posted by Genevieve Klien in category: security
Successful OmegaA test keeps the program on the path towards a 2021 first launch and a crack at the Air Force’s hotly contested national security launch program.
Jun 2, 2019
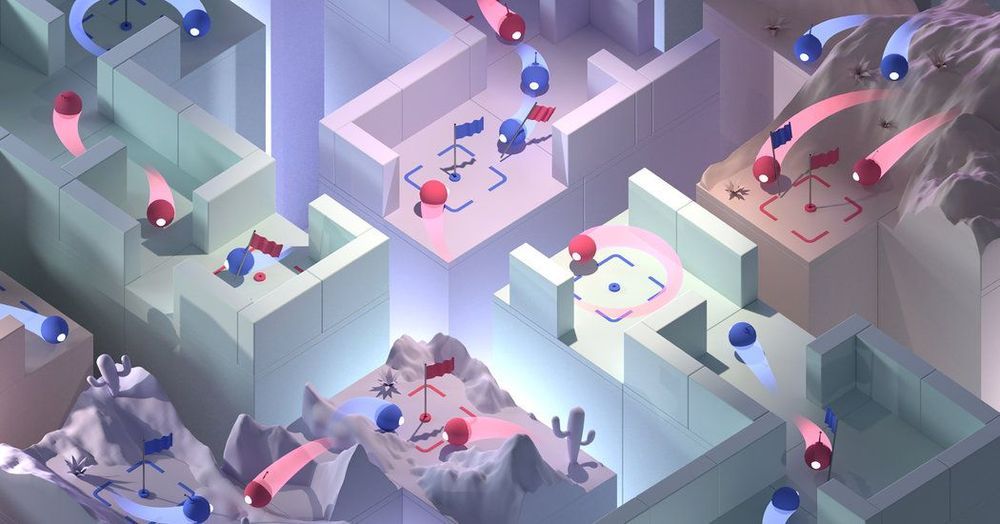
DeepMind Can Now Beat Us at Multiplayer Games, Too
Posted by Derick Lee in categories: entertainment, robotics/AI
As impressive as such technology has been among gamers, many artificial-intelligence experts question whether it will ultimately translate to solving real-world problems. DeepMind’s agents are not really collaborating, said Mark Riedl, a professor at Georgia Tech College of Computing who specializes in artificial intelligence. They are merely responding to what is happening in the game, rather than trading messages with one another, as human players do. (Even mere ants can collaborate by trading chemical signals.)
Chess and Go were child’s play. Now A.I. is winning at capture the flag. Will such skills translate to the real world?
Jun 1, 2019
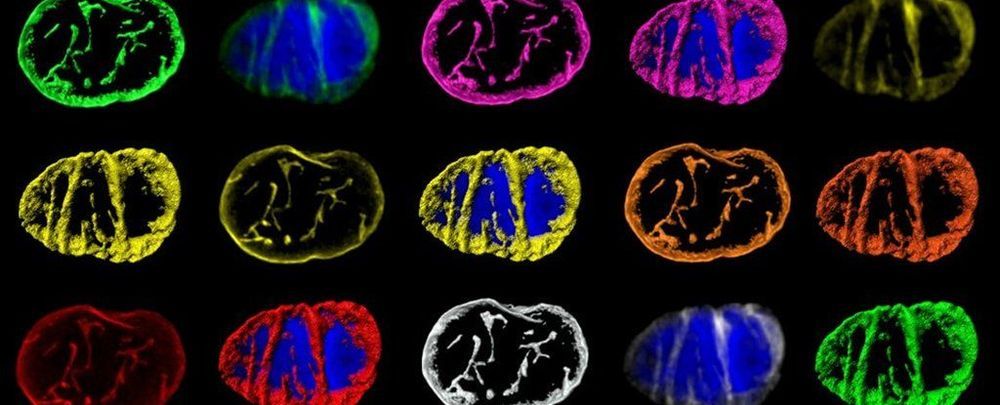
For The First Time Ever, Scientists Observe The Complex Messaging System of Cells
Posted by Paul Battista in categories: computing, employment, nanotechnology
The way information travels inside the cells of our bodies is not unlike the wiring inside a computer chip, according to a new study that has unveiled the intricate workings of a network of calcium ions as intracellular messengers.
According to researchers from the University of Edinburgh in the UK, this “cell-wide web” uses a microscopic network of guides to transmit information across nanoscale distances and carry activities and instructions for the cells to perform — such as relaxing or contracting muscles, for example.
Calcium ions (Ca2+) are a fundamental part of the messaging system of our cells, and their signals are crucial for a wide variety of jobs, including cell growth, death, and movement. Now researchers have taken an unprecedented close look at just how calcium ions shuttle messages within the cell.
Jun 1, 2019
New way to protect against high-dose radiation damage discovered
Posted by Paul Battista in categories: biotech/medical, military, space travel
Damage of healthy intestinal cells is the main disadvantage of radiotherapy leading to the discontinuation and failure of an efficient cancer treatment, potentially causing a quick tumour recurrence. Now, a discovery published in Science by scientists from the Growth Factors, Nutrients and Cancer Group at the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO) might be useful to protect healthy intestinal cells from radiation damage. The consequences of their findings in mice might radically change the way humans manage exposure to high levels of radiation; both for cancer research and treatment as well as for other areas like space explorations, nuclear warfare or nuclear accidents.
The Group’s work focuses on URI, a protein whose functions remain not yet fully understood. However, previous studies from the Group have found that abnormal levels of expression of this protein in certain organs can cause cancer. The study now published in Science shows that high levels of URI protein protect mice from radiation-induced intestinal damage, whereas low or no detectable levels of the protein can lead to gastrointestinal syndrome and death.
“The precise functions of URI have not been identified yet,” says Nabil Djouder, Head of the Growth Factors, Nutrients and Cancer Group at CNIO and leader of the study. “Just like pH or temperature, which the organism needs to maintain within a certain range, URI levels must also be kept within a very narrow window to regulate the proper functioning of other proteins. When URI levels are higher or lower than optimal, they may promote or protect against tumour development as well as other diseases, depending on the context.”
Continue reading “New way to protect against high-dose radiation damage discovered” »
Jun 1, 2019
Zolpidem arouses patients in vegetative state after brain injury: quantitative evaluation and indications
Posted by Paul Battista in categories: biotech/medical, neuroscience
Am J Med Sci. 2014 Mar;347:178–82. doi: 10.1097/MAJ.0b013e318287c79c.
BACKGROUND: To investigate the efficacy and indications of zolpidem, a nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic, inducing arousal in vegetative state patients after brain injury.
METHODS: One hundred sixty-five patients were divided into 4 groups, according to area of brain damage and injury mechanism. All patients’ brains were imaged by Tc-ECD single-photon emission computerized tomography (SPECT), before and 1 hour after treatment with 10 mg of zolpidem. Simultaneously, 3 quantitative indicators of brain function and damage were obtained using cerebral state monitor. Thirty-eight patients withdrew from the study after the first zolpidem dose. The remaining 127 patients received a daily dose of 10 mg of zolpidem for 1 week and were monitored again at the end of this week.
Jun 1, 2019
Artificial Intelligence Complete Courses (01−23) Patrick H. Winston
Posted by Müslüm Yildiz in category: robotics/AI
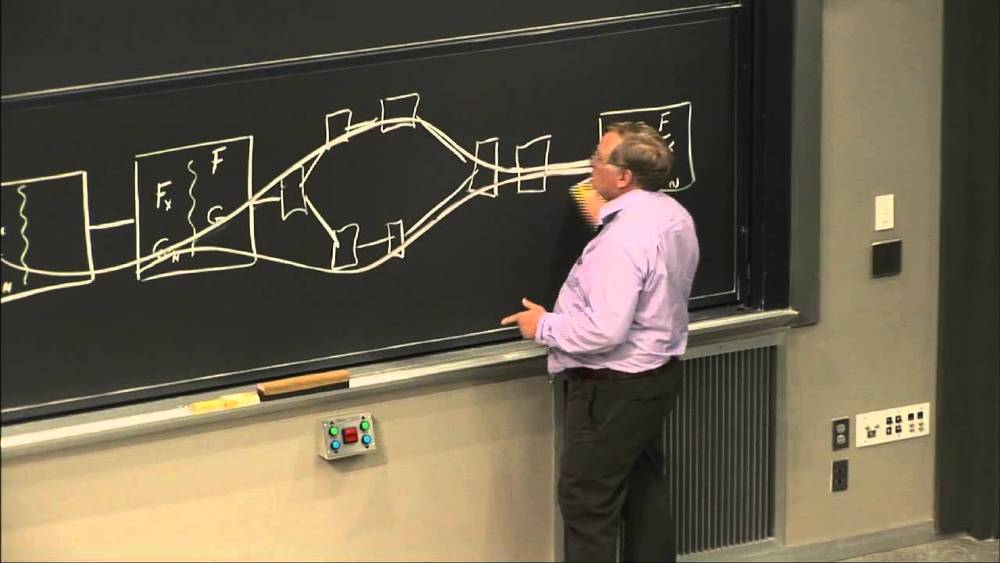
Prof. Patrick Henry Winston introduces students to the basic knowledge representation, problem solving, and learning methods of artificial intelligence.
Jun 1, 2019
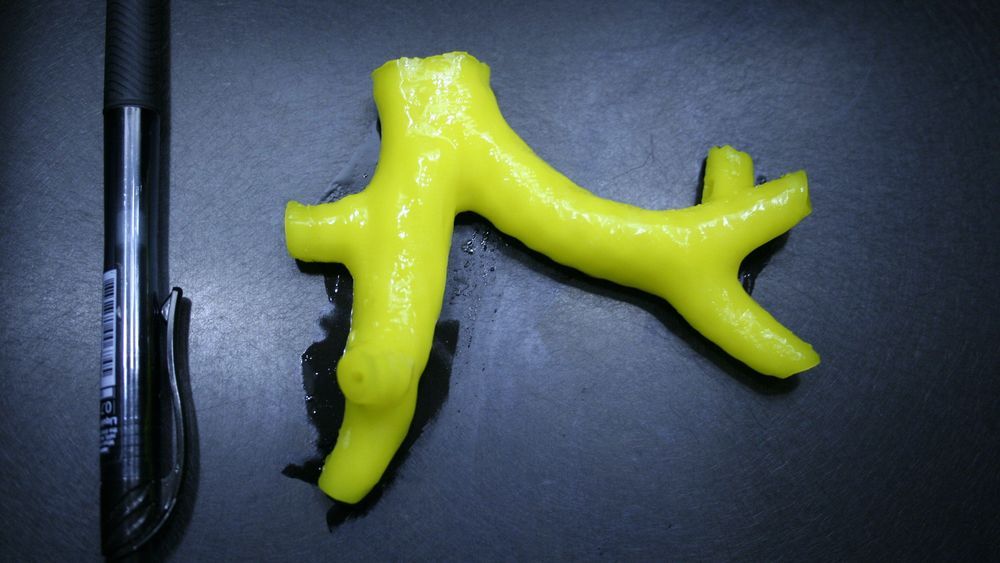
Inside the effort to print lungs and breathe life into them with stem cells
Posted by Paul Battista in categories: 3D printing, biotech/medical
Jun 1, 2019
Ep#141 – Cryonics: Surviving Death
Posted by Paul Battista in categories: cryonics, life extension
This week on The #GSPodcast Stephen Knight talks to microbiologist João Pedro de Magalhães (@jpsenescence) about Cryonics. They discuss the fear of dying, the science behind freezing humans, the implications for religion, technological advancements in the field and much, much more!
Support the podcast at http://www.patreon.com/gspellchecker
Jun 1, 2019
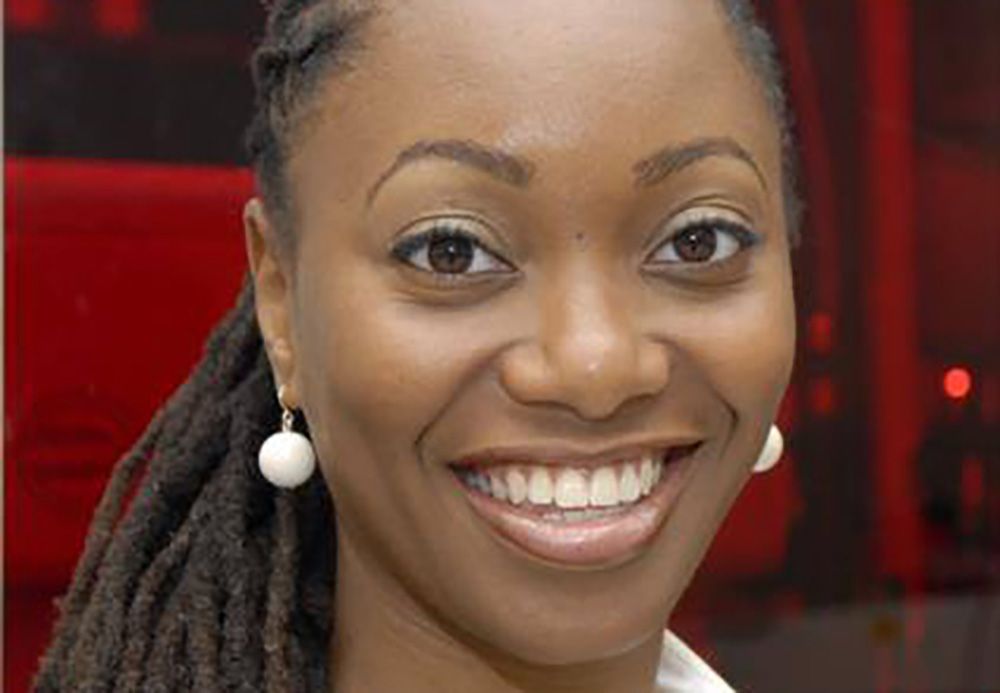
Black female physicist pioneers technology that kills cancer cells with lasers
Posted by Paul Battista in categories: biotech/medical, education, nanotechnology, neuroscience
Dr. Hadiyah-Nicole Green is one of fewer than 100 black female physicists in the country, and the recent winner of $1.1 million grant to further develop a technology she’s pioneered that uses laser-activated nanoparticles to treat cancer.
Green, who lost her parents young, was raised by her aunt and uncle. While still at school, her aunt died from cancer, and three months later her uncle was diagnosed with cancer, too. Green went on to earn her degree in physics at Alabama A&M University, being crowned Homecoming Queen while she was at it, before going on full scholarship to University of Alabama in Birmingham to earn her Masters and Ph.D. There Green would become the first to work out how to deliver nanoparticles into cancer cells exclusively, so that a laser could be used to remove them, and then successfully carry out her treatment on living animals.
As she takes on her growing responsibilities, Green still makes time to speak at schools, Boys & Girls Clubs and other youth events. “Young black girls don’t see those role models (scientists) as often as they see Beyonce or Nicki Minaj,” says Green. “It’s important to know that our brains are capable of more.”
Continue reading “Black female physicist pioneers technology that kills cancer cells with lasers” »