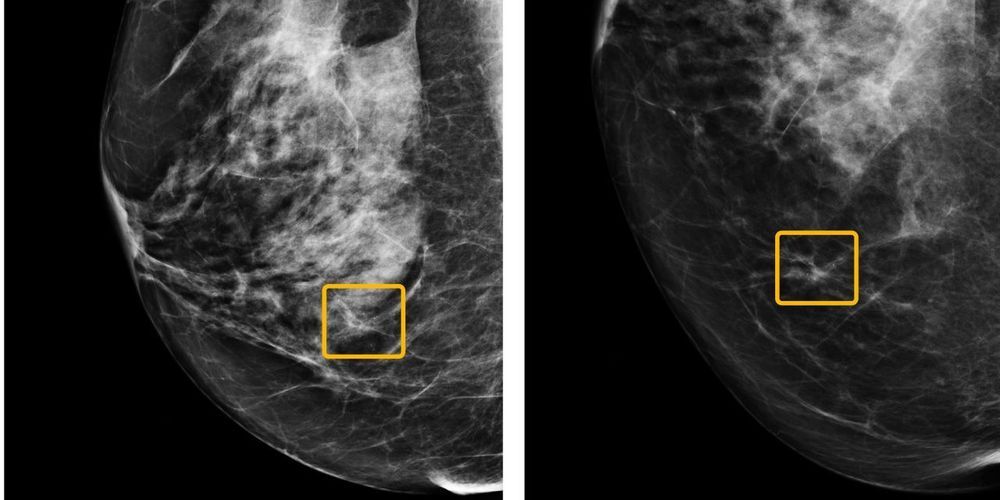
In a study published Jan. 1 in Nature, researchers from Google Health, and from universities in the U.S. and U.K., report on an AI model that reads mammograms with fewer false positives and false negatives than human experts. The algorithm, based on mammograms taken from more than 76,000 women in the U.K. and more than 15,000 in the U.S., reduced false positive rates by nearly 6% in the U.S., where women are screened every one to two years, and by 1.2% in the U.K., where women are screened every three years. The AI model also lowered false negatives by more than 9% in the U.S. and by nearly 3% in the U.K.
Working with medical experts, engineers at Google Health have created an AI model that lowers false positive and false negative rates for mammogram breast cancer screening.