Feb 20, 2020
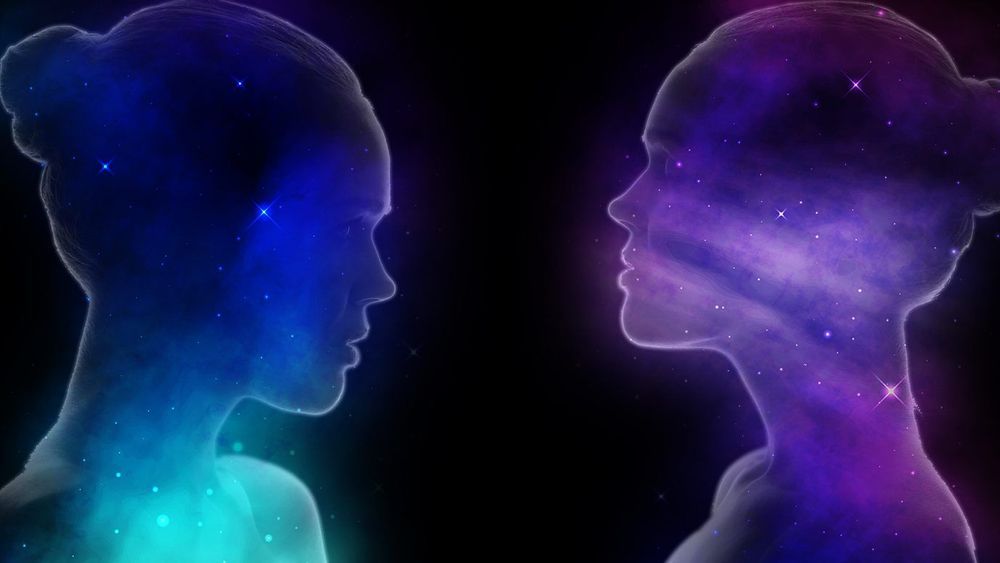
Does our Universe have a twin?
Posted by Paul Battista in categories: cosmology, physics
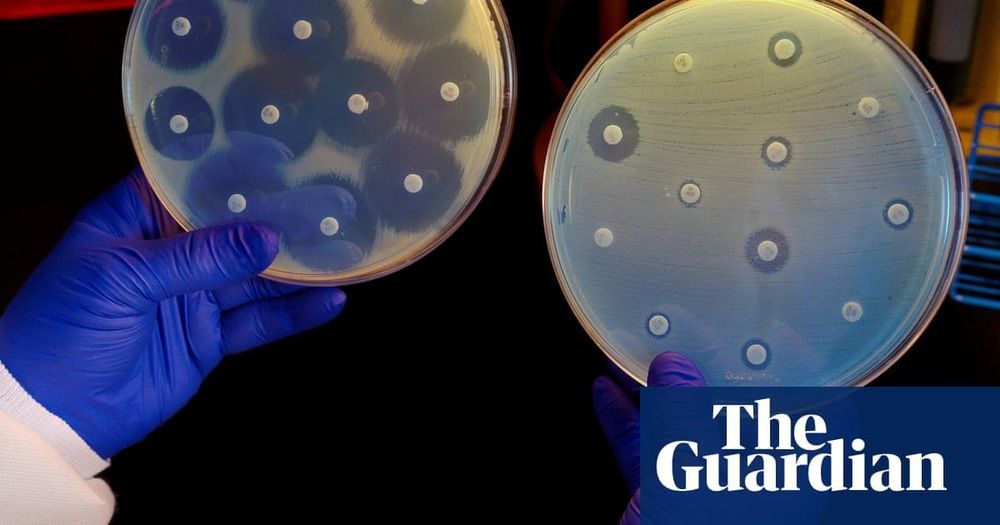
Is our Universe really the only one? A new theory that hopes to solve one of the biggest problems in physics, may have rewritten our perception of time, and found a way through the Big Bang. Video by Howard Timberlake.
Follow BBC Reel on Twitter and Facebook for all our latest videos.