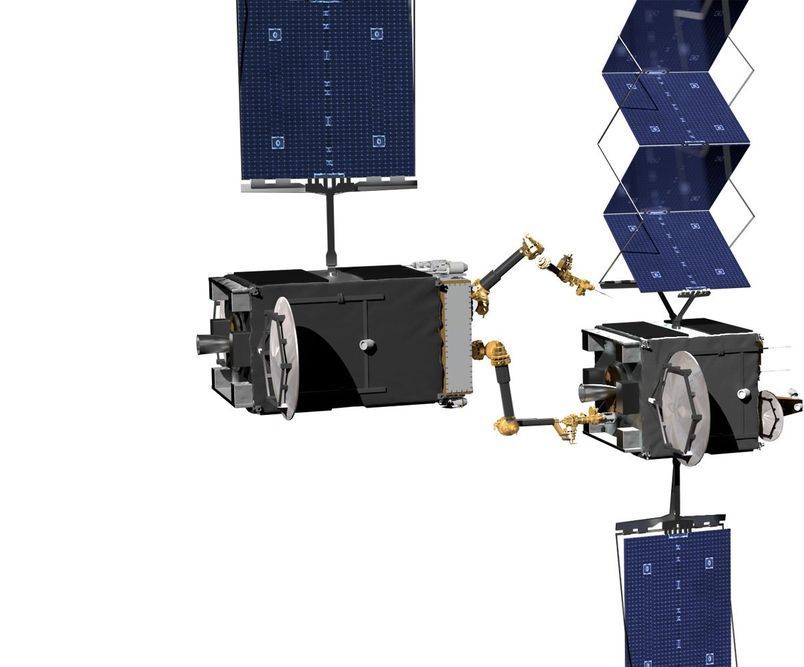
DARPA has entered into a partnership with Northrop Grumman subsidiary Space Logistics LLC to develop robotic technologies for servicing and extending the service lives of orbital satellites. Based on the Mission Extension Vehicle-1 (MEV-1), which recently docked with a communication satellite in geosynchronous orbit, the technology will be used by the agency’s Robotic Servicing of Geosynchronous Satellites (RSGS) program to develop a dexterous robotic servicer that would be operated by private companies.
Founded in 2016, the RSGS program completed a Payload Critical Design Review in 2019 and is developing key technologies in the run up to the first space launch scheduled for 2023. As part of this effort, DARPA says it is funding the US Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) to bring together components like the robotic manipulator arms, a variety of interchangeable tools, cameras, sensors, software, and avionics into a functioning robotic payload.
Meanwhile, Space Logistics will provide the spacecraft bus based on the MEV and integrate the robotic payload, as well as providing launch and orbital operation services. Once the spacecraft has been checked out and demonstrated its capabilities, the technology will be marketed to commercial and government organizations.