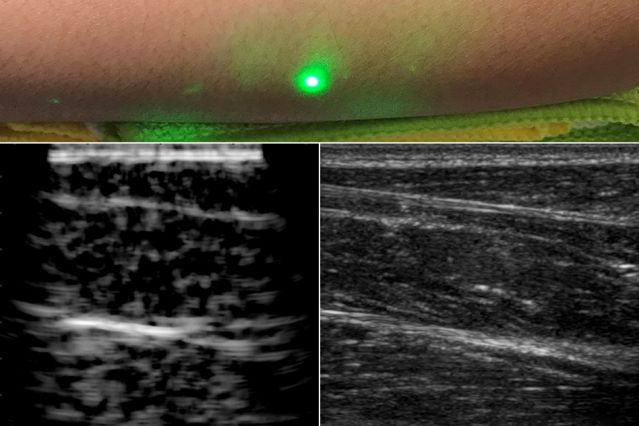
Researchers from MIT have revealed the very first images of a human generated through a novel laser ultrasound imaging technique. Unlike conventional ultrasound, the new technique does not require any skin contact with the body, dramatically amplifying the range of uses for doctors in clinical environments.
A conventional ultrasound is one of the cheapest and easiest imaging methods clinicians currently have in their arsenal. Unlike X-ray or CT scans, an ultrasound does not involve harmful radiation, and unlike PET or MRI scans, there is no need for large expensive machines. Of course, ultrasound does have a number of limitations, from the need for significant bodily contact in the process of imaging, to a variability in imaging results.
A new non-contact ultrasound method involving lasers has now been effectively demonstrated by a team of researchers from MIT. The challenge in developing the new method has been figuring out a way to use a laser to produce sound waves. Traditional ultrasound uses sound waves to penetrate a human body and bounce back off different tissues. Light, of course, cannot penetrate a human body as deeply as sound.