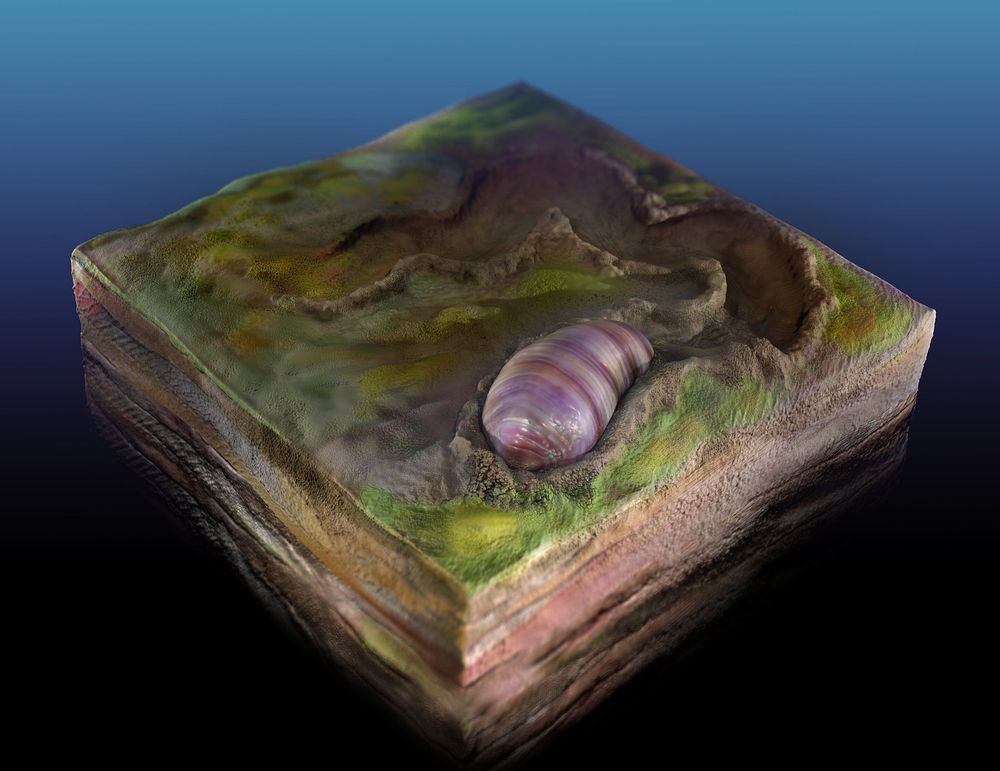
A team led by UC Riverside geologists has discovered the first ancestor on the family tree that contains most familiar animals today, including humans.
The tiny, wormlike creature, named Ikaria wariootia, is the earliest bilaterian, or organism with a front and back, two symmetrical sides, and openings at either end connected by a gut. The paper is published today in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The earliest multicellular organisms, such as sponges and algal mats, had variable shapes. Collectively known as the Ediacaran Biota, this group contains the oldest fossils of complex, multicellular organisms. However, most of these are not directly related to animals around today, including lily pad-shaped creatures known as Dickinsonia that lack basic features of most animals, such as a mouth or gut.