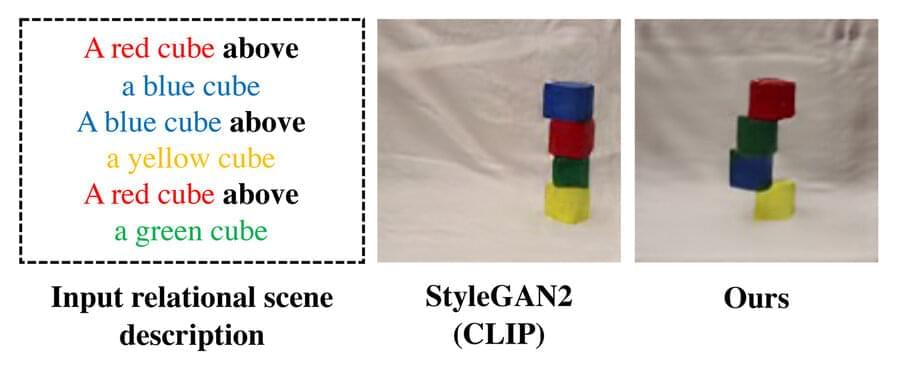
When humans look at a scene, they see objects and the relationships between them. On top of your desk, there might be a laptop that is sitting to the left of a phone, which is in front of a computer monitor.
Many deep learning models struggle to see the world this way because they don’t understand the entangled relationships between individual objects. Without knowledge of these relationships, a robot designed to help someone in a kitchen would have difficulty following a command like “pick up the spatula that is to the left of the stove and place it on top of the cutting board.”
In an effort to solve this problem, MIT researchers have developed a model that understands the underlying relationships between objects in a scene. Their model represents individual relationships one at a time, then combines these representations to describe the overall scene. This enables the model to generate more accurate images from text descriptions, even when the scene includes several objects that are arranged in different relationships with one another.