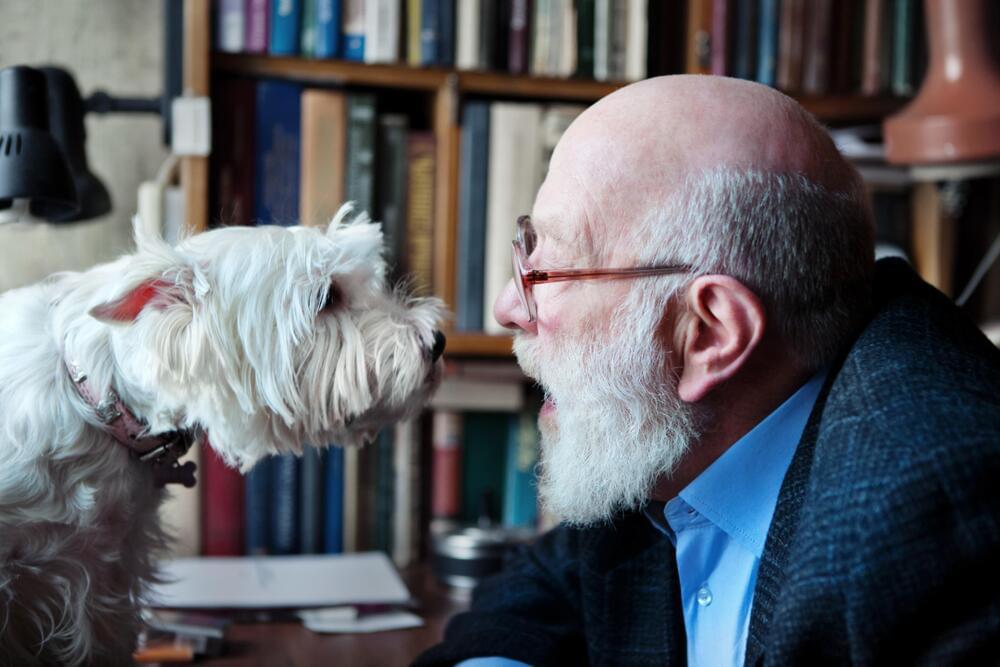
From the fMRI scans, the researchers saw the same areas of the brain light up but with different activation patterns, depending on whether the dogs were hearing the story in their native language or a new one—suggesting that they were neurologically processing differences between the two languages.
Then the researchers tried to test whether the dogs were responding to specific characteristics intrinsic to each language. Were the animals reacting to actual changes in speech patterns—that Hungarian words put stress on the first syllable, for instance—or just responding to basic differences in fundamental auditory signatures between the two languages—alterations in tones that occur during vowel pronunciation? They tested this by playing recordings in which the speech from the story had been garbled, resulting in gibberish that “sounded” like Hungarian or Spanish. Again, the team saw different patterns in brain activity when a dog heard real human speech instead of speechlike gibberish, although the researchers cannot yet say whether this is evidence that dogs can recognize human speech as speech (sounds strung together in a meaningful way for humans to communicate with one another)—or whether their brain was just responding to the more natural sound when compared with the weird-sounding gibberish. There was no change in brain activity between hearing Spanish gibberish versus Hungarian gibberish, however, implying that the canines’ brain was not just responding to the different tonal qualities.”
A new study’s authors say their investigation represents the first time that a nonhuman brain has been shown to detect language.
Continue reading “Dogs Can Distinguish Speech from Gibberish—and Tell Spanish from Hungarian” »