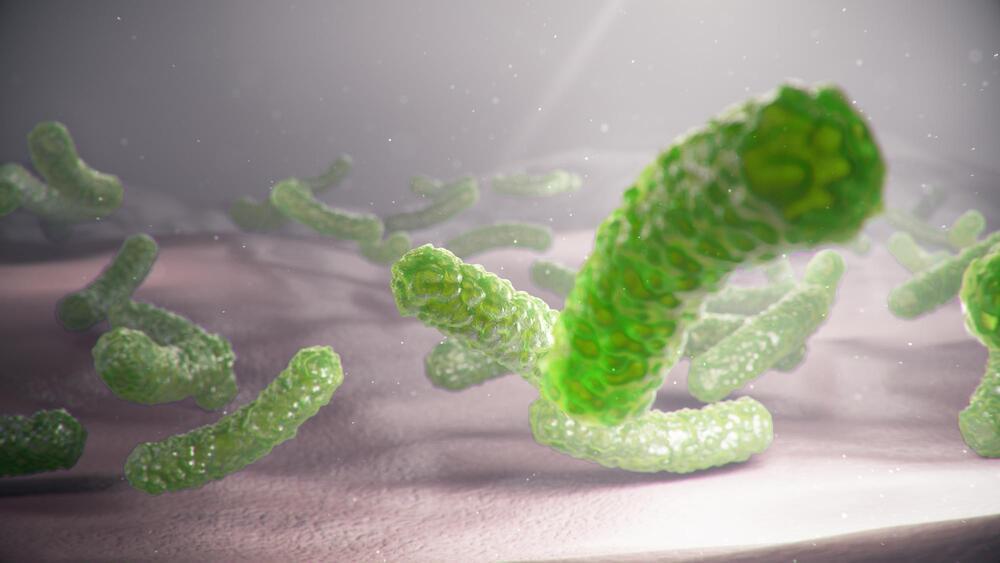
Biologists have discovered the largest bacterium ever found, with a single cell measuring a mammoth 2 cm (0.8 in) long. Visible to the naked eye, this new species has some bizarre characteristics that make it like a missing link in the evolution of complex cells like those in humans.
Most species of bacteria measure between one and five micrometers long, but the biggest previously known was Thiomargarita namibiensis, which tops out at 750 micrometers or 0.75 mm. But this newly identified species blows everything else out of the water – its average length is a whopping 9,000 micrometers (0.9 cm/0.4 in), with the largest recorded specimen reaching 2 cm. This single cell is longer than your everyday housefly.
This gigantic size completely upends the accepted scientific understanding of how big bacteria could possibly get. It was long believed that the size of bacteria was limited by the distance that the molecules they exchange with their environment could travel. If nutrients can’t make the journey from their membrane to their interior, and if toxins can’t do the reverse trip, the organism wouldn’t be viable.

















