Mar 9, 2022
DNA Replication Speed Limit Could Be a Breakthrough for Stem Cell Therapy
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: biotech/medical, innovation
Adult cells in our body can only give rise to the same cell type. For example, a skin cell cannot give rise to a muscle cell but to skin cells only. This limits the potential use of adult cells for therapy. During early development, however, the cells in the embryo have the capacity to generate all cell types of our body, including stem cells. This capacity, which is called totipotency, has served as an inspiration for researchers to find new ways to recapitulate totipotency through cellular reprogramming in the lab.
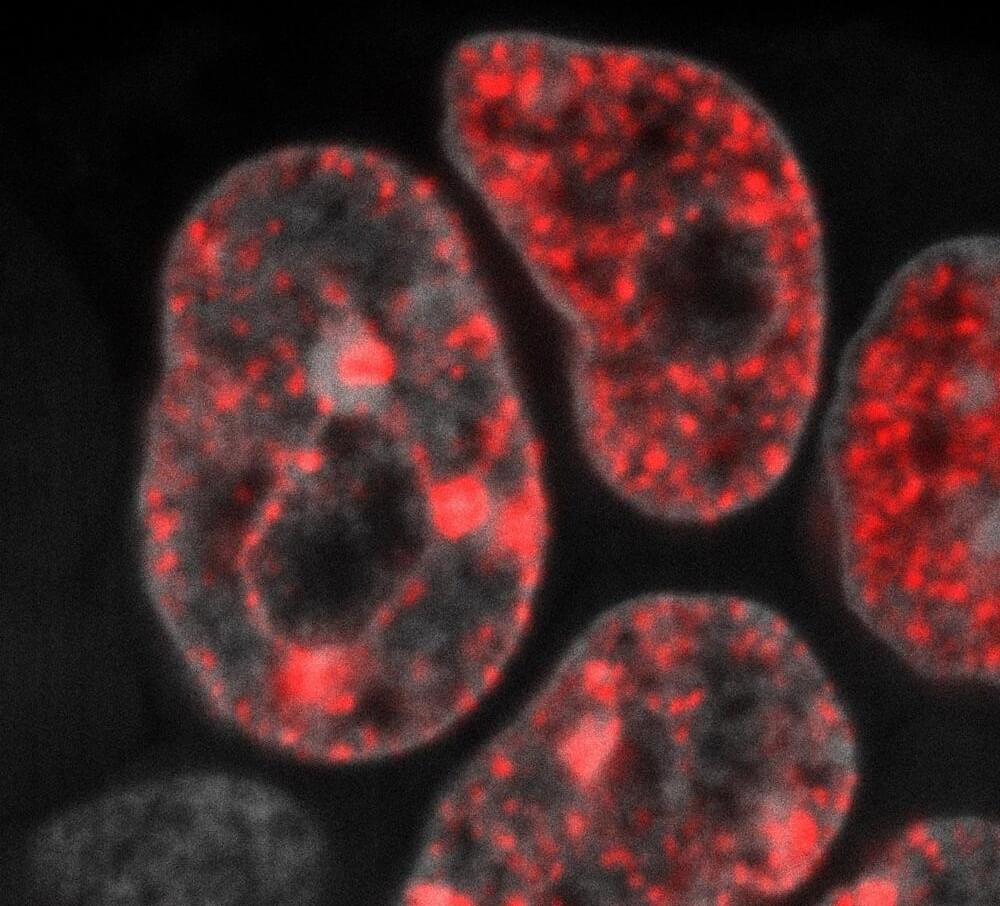
Totipotent cells have their own speed
Totipotent cells have many properties, but we do not know all of them yet. Researchers at Helmholtz Munich have now made a new discovery: “We found out that in totipotent cells, the mother cells of stem cells, DNA replication occurs at a different pace compared to other more differentiated cells. It is much slower than in any other cell type we studied,” says Tsunetoshi Nakatani, first-author of the new study.