Mar 21, 2022
Planetary Defense at NASA
Posted by Alan Jurisson in categories: asteroid/comet impacts, existential risks
Wed, Mar 23 at 10 PM CDT.
GUEST SPEAKERS:
Kelly fast, near-earth object observations program manager, NASA
Wed, Mar 23 at 10 PM CDT.
GUEST SPEAKERS:
Kelly fast, near-earth object observations program manager, NASA
For self-driving cars and other applications developed using AI, you need what’s known as “deep learning”, the core concepts of which emerged in the ’50s. This requires training models based on similar patterns as seen in the human brain. This, in turn, requires a large amount of compute power, as afforded by TPUs (tensor processing units) or GPUs (graphics processing units) running for lengthy periods. However, cost of this compute power is out of reach of most AI developers, who largely rent it from cloud computing platforms such as AWS or Azure. What is to be done?
Well, one approach is that taken by U.K. startup Gensyn. It’s taken the idea of the distributed computing power of older projects such as SETI@home and the COVID-19 focussed Folding@home and applied it in the direction of this desire for deep learning amongst AI developers. The result is a way to get high-performance compute power from a distributed network of computers.
Gensyn has now raised a $6.5 million seed led by Eden Block, a web3 VC. Also participating in the round is Galaxy Digital, Maven 11, Coinfund, Hypersphere, Zee Prime and founders from some blockchain protocols. This adds to a previously unannounced pre-seed investment of $1.1 millionin 2021 — led by 7percent Ventures and Counterview Capital, with participation from Entrepreneur First and id4 Ventures.
Four-legged robots are nothing novel — Boston Dynamics’ Spot has been making the rounds for some time, as have countless alternative open source designs. But with theirs, researchers at MIT claim to have broken the record for the fastest robot run recorded. Working out of MIT’s Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL), the team says that they developed a system that allows the MIT-designed Mini Cheetah to learn to run by trial and error in simulation.
While the speedy Mini Cheetah has limited direct applications in the enterprise, the researchers believe that their technique could be used to improve the capabilities of other robotics systems — including those used in factories to assemble products before they’re shipped to customers. It’s timely work as the pandemic accelerates the adoption of autonomous robots in industry. According to an Automation World survey, 44.9% of the assembly and manufacturing facilities that currently use robots consider the robots to be an integral part of their operations.
Today’s cutting-edge robots are “taught” to perform tasks through reinforcement learning, a type of machine learning technique that enables robots to learn by trial and error using feedback from their own actions and experiences. When a robot performs a “right” action — i.e., an action that’ll lead it toward a desired goal, like stowing an object on a shelf — it receives a “reward.” When it makes a mistake, the robot either doesn’t receive a reward or is “punished” by losing a previous reward. Over time, the robot discovers ways to maximize its reward and perform actions that achieve the sought-after goal.
Ever since last year’s annual American Association of Cancer Research (AACR) meeting, Volastra’s phone has been “ringing off the hook,” according to CEO Charles Hugh-Jones, M.D. | Two years since its inception, Volastra Therapeutics is partnering with Bristol Myers Squibb for up to three oncology targets focused on chromosomal instability, a deal that could exceed $1.1 billion should the assets hit milestones.
The researchers simulated the molecules H4, molecular nitrogen, and solid diamond. These involved as many as 120 orbitals, the patterns of electron density formed in atoms or molecules by one or more electrons. These are the largest chemistry simulations performed to date with the help of quantum computers.
A classical computer actually handles most of this fermionic quantum Monte Carlo simulation. The quantum computer steps in during the last, most computationally complex step—calculating the differences between the estimates of the ground state made by the quantum computer and the classical computer.
The prior record for chemical simulations with quantum computing employed 12 qubits and a kind of hybrid algorithm known as a variational quantum eigensolver (VQE). However, VQEs possess a number of limitations compared with this new hybrid approach. For example, when one wants a very precise answer from a VQE, even a small amount of noise in the quantum circuitry “can cause enough of an error in our estimate of the energy or other properties that’s too large,” says study coauthor William Huggins, a quantum physicist at Google Quantum AI in Mountain View, Calif.
Combining multiple data streams into one feed could speed up networks and let them tackle more than one task at a time.
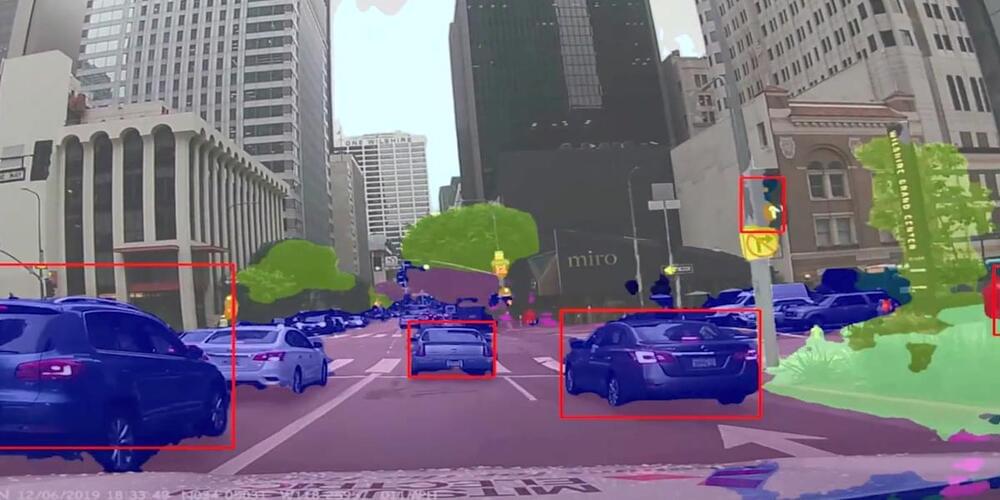
Mitsubishi’s AI not only improves performance, it also fosters trust.
Mitsubishi’s Electric AI not only improves performance, it also fosters trust.
Scientists have created the world’s smallest antenna, measuring only five nanometers in length, out of synthetic DNA.
But it doesn’t transmit radio waves — instead, this little antenna is designed to signal real-time changes in proteins. And because it’s fluorescent, it records and transmits data via light signals.
Treating brain diseases is also always difficult because of something called the “blood-brain barrier.” This wall of cells is designed to prevent toxins and pathogens from getting from the blood into the brain — but it also makes it hard to get treatments into the brain.
People with the Icelandic mutation are five times more likely to reach their 85 birthday without an Alzheimer’s diagnosis.
The Icelandic variant: Scientists have identified a couple of differences between the brains of people with Alzheimer’s and those of healthy people.

Dr. Michio Kaku on what is likely and what is possible provides a stimulating vision of the future.
