Follow these tips to help you improve your focus, memory and creative problem-solving ability so you can get smarter and wiser.



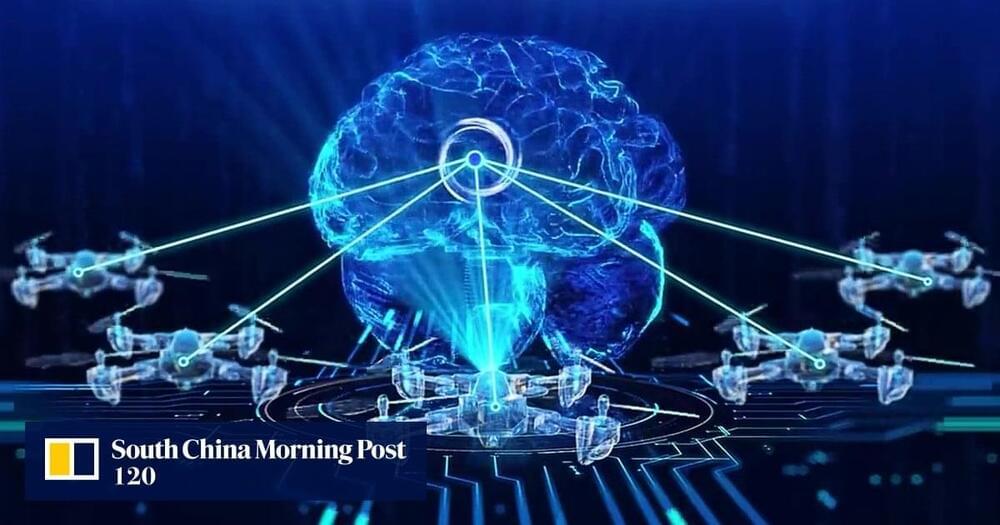
The post included a demonstration video from the researchers, showing how a team of five drones successfully located a set of keys in an outdoor park.
“The drones showcased key abilities, including humanlike dialogue interaction, proactive environmental awareness and autonomous entity control,” the WeChat report said. Autonomous entity control refers to the drone cluster’s ability to adjust flight status in real time based on environmental feedback.
The technology equips each drone with a “human brain”, allowing them to chat with each other using natural language. This ability was developed based on a Chinese open-source large language model called InternLM, according to the report.
Illuminating a high-resolution lens with waves whose intensity diminishes over time can improve the image quality.
Images formed using a conventional lens have a strict resolution limit—features smaller than about one half of a wavelength of light are lost. “Superlenses” made from structures called metamaterials could potentially beat this restriction if not for unavoidable losses in the transmission of the light carrying the finest details. Now researchers have used sound waves to demonstrate a new way around this problem that should also apply to light waves: they varied the amplitude of the “illuminating” waves over time [1]. The new approach, they believe, will enable the development of more precise acoustic and photonic lenses for use in areas such as microscopy and ultrasound imaging.
Not all of the light that reflects off of an object escapes to distances far away. The so-called evanescent waves decay rapidly in amplitude as they travel away from an object, but these waves contain the subwavelength information required to beat the usual resolution limit. A technique called near-field scanning optical microscopy can detect these waves by using a probe to scan across the object at close range, but real-time images are not possible because the scanning process is time consuming. Other “superresolution” imaging techniques also face trade-offs between complexity, speed, and efficiency.
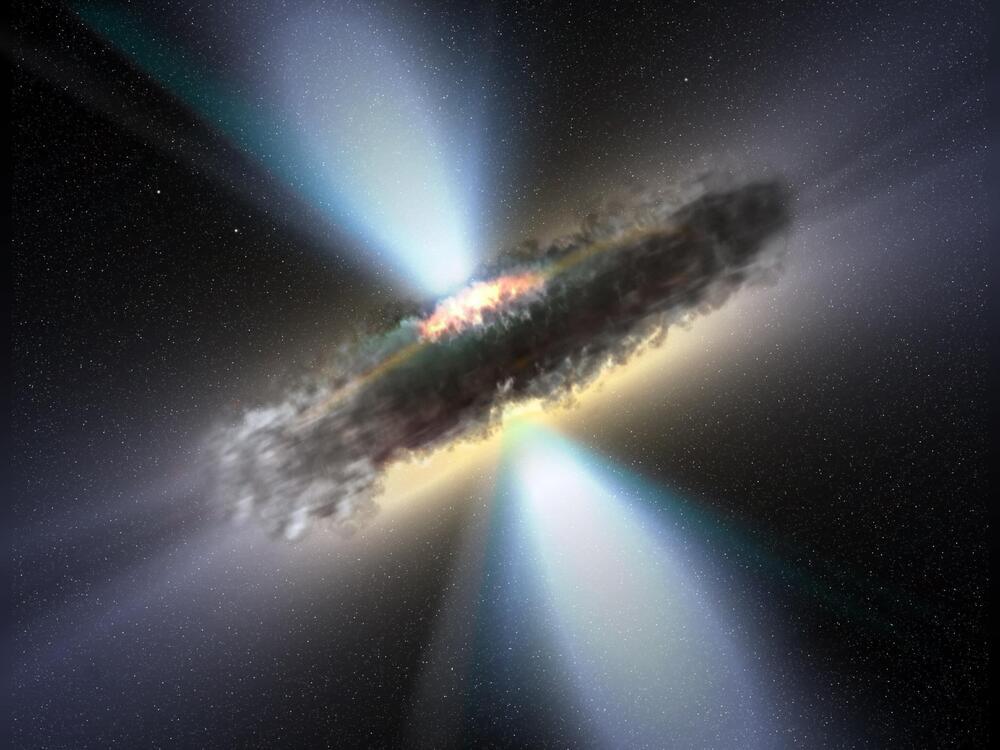

A new study reveals that supermassive black holes at the centers of galaxies, known as quasars, can sometimes be obscured by dense clouds of gas and dust in their host galaxies.
This challenges the prevailing idea that quasars are only obscured by donut-shaped rings of dust in the close vicinity of the black hole.
Quasars are extremely bright objects powered by black holes gorging on surrounding material. Their powerful radiation can be blocked if thick clouds come between us and the quasar.
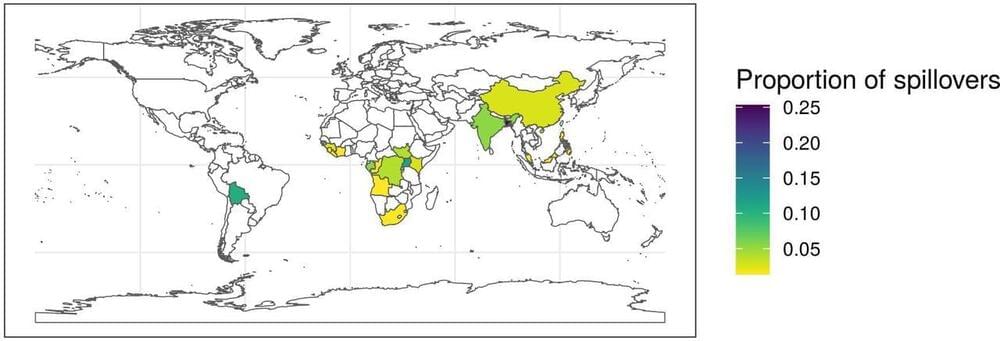
The COVID-19 pandemic has focused attention on patterns of infectious disease spillover. Climate and land-use changes are predicted to increase the frequency of zoonotic spillover events, which have been the cause of most modern epidemics. Characterising historical trends in zoonotic spillover can provide insights into the expected frequency and severity of future epidemics, but historical epidemiological data remains largely fragmented and difficult to analyse. We utilised our extensive epidemiological database to analyse a specific subset of high-consequence zoonotic spillover events for trends in the annual frequency and severity of outbreaks. Our analysis, which excludes the ongoing SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, shows that the number of spillover events and reported deaths have been increasing by 4.98% (confidence interval [CI]95% [3.22%; 6.76%]) and 8.7% (CI 95% [4.06%; 13.62%]) annually, respectively. This trend can be altered by concerted global efforts to improve our capacity to prevent and contain outbreaks. Such efforts are needed to address this large and growing risk to global health.

Isolate thin flakes that can be tuned to exhibit three important properties.
MIT is an acronym for the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. It is a prestigious private research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts that was founded in 1861. It is organized into five Schools: architecture and planning; engineering; humanities, arts, and social sciences; management; and science. MIT’s impact includes many scientific breakthroughs and technological advances. Their stated goal is to make a better world through education, research, and innovation.
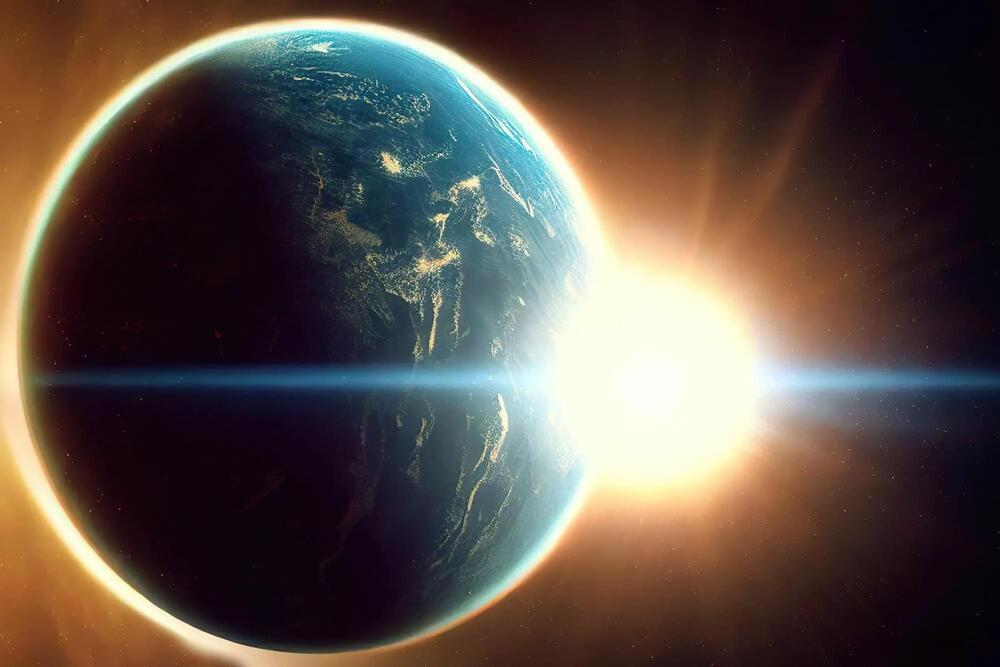

Things may not have ended well for dinosaurs on Earth, but Cornell University astronomers say the “light fingerprint” of the conditions that enabled them to emerge here provide a crucial missing piece in our search for signs of life on planets orbiting alien stars.
Their analysis of the most recent 540 million years of Earth’s evolution, known as the Phanerozoic Eon, finds that telescopes could better detect potential chemical signatures of life in the atmosphere of an Earth-like exoplanet.
An exoplanet (or extrasolar planet) is a planet that is located outside our Solar System, orbiting around a star other than the Sun. The first suspected scientific detection of an exoplanet occurred in 1988, with the first confirmation of detection coming in 1992.

Harnessing and controlling light plays a pivotal role in technological advancement, impacting energy harvesting, computation, communications, and biomedical sensing. Nevertheless, in real-world scenarios, the intricate behavior of light presents challenges for efficient control.
Physicist Andrea Alù draws a parallel between the behavior of light in chaotic systems and a game of billiards, where slight variations in the cue ball’s launch result in different ball trajectories on the table.
“In billiards, tiny variations in the way you launch the cue ball will lead to different patterns of the balls bouncing around the table,” said Alù, Einstein Professor of Physics at the CUNY Graduate Center, founding director of the Photonics Initiative at the CUNY Advanced Science Research Center and distinguished professor at CUNY. “Light rays operate in a similar way in a chaotic cavity. It becomes difficult to model to predict what will happen because you could run an experiment many times with similar settings, and you’ll get a different response every time.”